
Investing in mutual funds is one of the simplest and most popular ways to grow your wealth. It gives you access to a diversified portfolio while keeping costs in check. Traditionally, the success of a fund has largely depended on the skills and experience of its fund manager, someone who can steer through market ups and downs. But what if we could take the human element out of the equation and let numbers, algorithms, and data do the heavy lifting? Sounds intriguing, right? That is exactly what quant funds aim to do. Check out this blog to explore how quant funds work and whether algorithm-driven investing can truly match or even outperform the human touch in mutual fund investing.

Quant Mutual Funds are a type of mutual fund where investment decisions are made by computer algorithms and mathematical models instead of human fund managers. These algorithms analyse large amounts of data, like stock prices, company performance, and market trends, to decide which stocks or assets to buy or sell. The idea is to take emotions out of investing and rely purely on logic and statistics. Quant funds are a relatively new concept in India and have been gaining popularity over the last decade. While traditional mutual funds have always depended on the expertise and judgment of fund managers, investors are increasingly showing interest in quant funds because they promise a disciplined, data-driven approach that can potentially reduce human bias and improve consistency in returns.
Quant funds use the power of computational thinking and hard data to make strategic investment decisions. This makes it especially attractive, given the rise in algorithmic trading and the use of algorithms among new-age investors. The top features of quant funds are explained hereunder.
Quant funds rely on computer algorithms and mathematical models to make investment decisions. Unlike traditional funds, which depend on a fund manager’s judgment and experience, quant funds remove emotions from the process. The algorithm follows a logical, data-based approach to decide which stocks or assets to buy and sell. This helps maintain discipline and consistency in investment decisions.
These funds analyse large amounts of data, including stock prices, financial statements, economic indicators, and market trends. The algorithm identifies patterns and opportunities that may not be obvious to human investors. By relying on data rather than speculation or hearsay, quant funds aim to make more informed and objective investment choices.
As quant funds operate based on predefined rules and algorithms, investment decisions are objective and less prone to bias. Investors can understand the basic logic behind the fund’s strategy, which makes it more transparent than traditional actively managed funds, where decisions may be influenced by the fund manager’s personal views.
Quant funds usually invest across multiple stocks, sectors, or asset classes. The algorithm carefully selects a diversified portfolio to spread risk, so that losses in one stock or sector do not heavily impact the overall fund. This diversification can help protect investors’ money in volatile markets.
Quant funds often have risk controls built into their algorithms. For example, the model may limit exposure to highly volatile stocks or avoid concentration in a single sector. This built-in risk management helps maintain a balanced and safer portfolio for investors.
Human emotions like fear or greed can often lead to impulsive investment decisions. Quant funds remove this emotional element, reducing the risk of biased or irrational choices. This can result in more consistent performance over time, especially during periods of market uncertainty.
Since the fund relies on automated algorithms rather than constant human intervention, operational costs can be lower. Some of these savings may be passed on to investors in the form of lower expense ratios, making quant funds a cost-effective choice for many.
Before being applied in real markets, the algorithms are often tested on historical data. This ‘backtesting’ helps fund managers understand how the model might perform in different market scenarios. It provides confidence that the strategy can handle both bullish and bearish phases.
Quant funds can implement advanced investment strategies such as momentum investing, value investing, or factor-based investing. These strategies may be complex for humans to execute consistently, but can be automated using algorithms, allowing investors to benefit from innovative approaches to growing their wealth.
Quant funds are essentially divided into two main categories, like traditional funds, i.e, active funds and passive funds. However, quant funds are algorithm-based and can be further classified based on the parameters or factors that are used to design the investment objective. The details of the types of quant funds are explained below.
Active quant funds are managed using algorithms that actively make investment decisions based on market data, stock performance, and other financial indicators. The algorithm continuously analyses the market and decides which stocks or assets to buy, hold, or sell to try to generate higher returns than a benchmark index. Unlike traditional active funds managed by humans, these funds rely entirely on data-driven models, removing emotional bias from the investment process. Investors who want the potential for higher returns but with a systematic approach often choose active quant funds.
Passive quant funds, on the other hand, aim to track or replicate a market index, like the Nifty 50 and Sensex, but they use algorithms to automate this process. Instead of trying to beat the market, passive quant funds follow the market in a disciplined and cost-effective way. These funds are suitable for investors who prefer long-term growth with lower management costs and minimal risk from human error or bias.
Single-factor quant funds focus on one specific investment factor or characteristic while selecting stocks. Common factors include value (buying undervalued stocks), momentum (investing in stocks showing strong trends), quality (selecting financially strong companies), or low volatility (choosing stable stocks). The algorithm identifies stocks that score well on the chosen factor and builds the portfolio accordingly. Investors looking for a focused, rule-based approach in one particular area of investing often prefer single-factor quant funds.
Multi-factor quant funds use multiple factors simultaneously to select stocks, such as combining value, momentum, quality, and low volatility. The algorithm balances these factors to create a diversified portfolio that aims to reduce risk and enhance returns. By considering several factors together, these funds can potentially perform more consistently across different market conditions. Multi-factor quant funds appeal to investors who want a systematic approach that spreads risk while targeting better long-term performance.
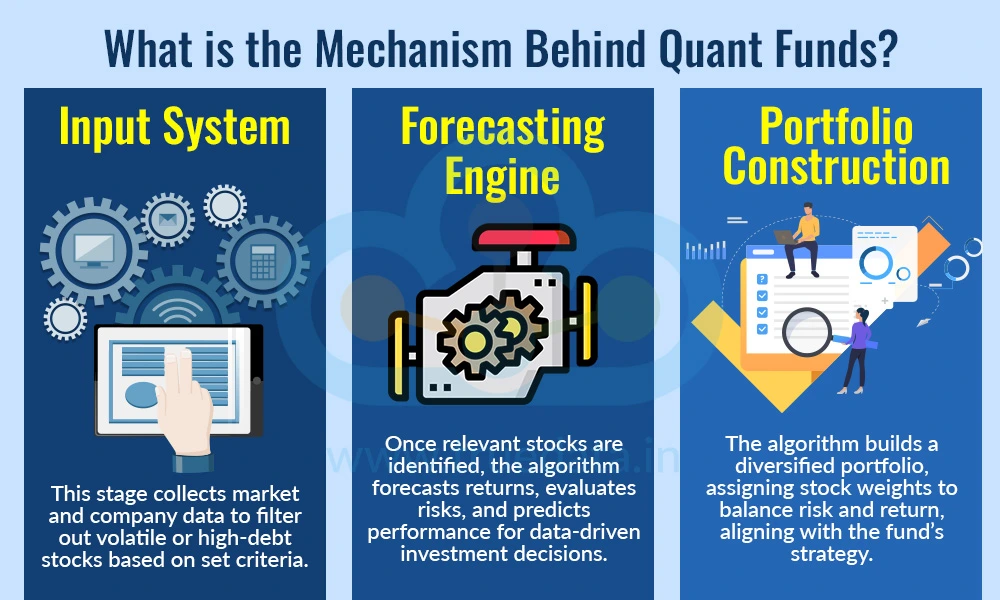
Quant mutual funds use a systematic, data-driven approach to investing, removing emotions from decision-making. They begin by collecting large amounts of historical and real-time market data, including stock prices, company financials, and macroeconomic indicators like interest rates, GDP growth, and inflation, which form the foundation for investment decisions. Advanced mathematical models and algorithms are then developed to analyse this data, identifying patterns, correlations, and trends that highlight potential investment opportunities while managing risk. Based on these insights, the fund creates systematic strategies, like focusing on stocks with strong earnings or low risk, to decide which stocks to buy, when to trade, and how to balance the portfolio. Finally, these models and strategies undergo continuous testing, refinement, and updates with new data, allowing the fund to adapt to changing market conditions and maintain consistent, disciplined performance over time.
This quantitative investment process for quant funds can thus be categorised under the following three stages.
Input System - In this stage, essential market and company-specific data is collected. Market data can include indicators like interest rates, GDP growth, and inflation, while company data includes earnings, revenue growth, debt levels, and P/E ratios. The algorithm uses this information to filter out stocks that do not meet the chosen criteria. For example, highly volatile stocks or companies with excessive debt may be excluded from consideration.
Forecasting Engine - Once the relevant stocks are identified, the algorithm estimates their expected performance. This includes calculating potential returns, evaluating risks, and assessing other performance factors. By forecasting how each stock might behave under different market conditions, the fund can make more informed and data-backed investment decisions.
Portfolio Construction - The final stage involves building the actual investment portfolio. Using optimisation techniques, the algorithm assigns appropriate weights to each selected stock to balance risk and return. Depending on the scheme, the final stock selection may still involve some input from the fund manager, or the process may be fully automated. The main goal is to construct a diversified, well-balanced portfolio that aligns with the fund’s strategy and objectives.

The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) plays a vital role in regulating mutual funds, including quant funds, to ensure transparency, market integrity, and investor protection. With the rise of algorithm-driven investing, SEBI has introduced rules that balance innovation with safety, ensuring that algorithms and quantitative strategies operate responsibly in India’s financial markets. These rules include,
All trading algorithms used by quant funds must be registered and approved by stock exchanges before they are deployed. This ensures that the algorithms operate safely without causing market disruptions or generating erroneous trades. SEBI’s approval process helps maintain confidence in algorithmic investing.
Each algorithm is assigned a unique identifier, which is attached to every order it executes. This ‘digital license plate’ allows SEBI to trace and investigate incidents such as unexpected market fluctuations caused by coding errors. This system enforces accountability and ensures transparency in automated trading.
SEBI classifies algorithms used for quant funds as White Box (fully transparent, rule-based) or Black Box (proprietary logic with limited disclosure). SEBI further mandates providers of black box models to register as research analysts and regularly report their models. This provision is to ensure adherence to the core responsibility of SEBI, i.e., protection of investors’ interests and preventing unverified claims of guaranteed returns, thus ensuring that even proprietary algorithms adhere to regulatory standards.
Brokers act as gatekeepers for quant funds by requiring pre-approval of algorithms, monitoring trades in real time, and maintaining emergency ‘kill switches’ to halt malfunctioning algorithms. SEBI also mandates secure API access, allowing only authorised IP addresses and OAuth-based logins. These measures protect trading infrastructure from unauthorised use and technical risks.
Quant funds must clearly disclose their investment strategy, including the use of algorithms, in their scheme documents. SEBI requires strict adherence to the stated strategy, proper portfolio diversification, and risk management practices. Regular reporting of fund holdings, performance, and strategy changes ensures investors are well-informed at all times.
SEBI continues to approve new quant-based mutual fund schemes, signalling support for the growth of this investment segment. At the same time, regulatory requirements ensure that these funds operate responsibly, protecting investors and preserving the integrity of the Indian financial markets.

Now that we have explored the various details of quant funds, let us address the target investors for these funds.
Investors seeking data-driven decisions rather than human judgment.
Long-term investors looking for disciplined, consistent growth over time through the systematic approach of quant funds.
Risk-averse investors who want diversified portfolios with built-in risk management.
Busy professionals who may not have the time to monitor markets daily.
Investors seeking transparency and rule-based strategies backing investment decisions.
Investor with moderate to high risk appetite.
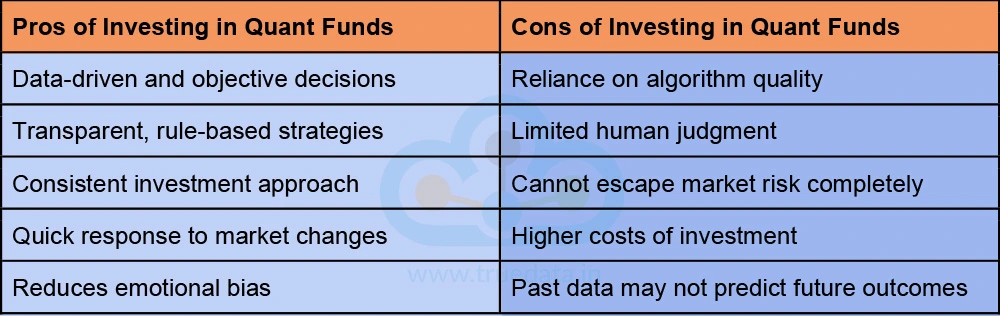
The pros and cons of investing in quant funds help investors to understand the advantages as well as the cautions against this investment, thereby helping them make informed investment decisions. Some of the benefits and limitations of investing in quant funds are tabled below.
Quant funds are the next step of evolution in mutual funds. They focus on data-driven investment strategies by relying on algorithms and mathematical models rather than human judgment. While they are relatively new to the Indian investment scenario, strong SEBI regulations and review ensure that the investors’ interests are protected amidst the technical framework of the fund. Thus, quant funds offer an innovative and disciplined alternative to traditional mutual funds, making them appealing to new-age investors who focus on technology, transparency, and a structured approach to growing wealth.
This article explains quant-based funds, which are being seen as the newage form of investing to take your portfolio to new levels. Let us know your thoughts on this topic or if you have any queries on the same, and we will address them.
Till then, Happy Reading!
Read More: Rise of Silver Lithium and Energy - Thematic Mutual Funds

Mutual fund investments have simplified greatly with just a tap on your smartpho...

Mutual fund investments have simplified greatly with just a tap on your smartpho...
Introduction For the longest time, investment in stock markets was thought to b...