
Did you know that stock trading is fast becoming one of the most popular searches for young graduates and professionals looking for side gigs? This is a completely different scenario compared to only a few years ago when stock trading was equated to gambling. The new-age trading platforms and ease of trading in real-time are some of the prime reasons for this increase. Another prominent reason is Algo Trading. Have you heard about it? Check out this blog to know all about Algo Trading and its related details.

Algorithmic trading, commonly known as algo trading, refers to the use of computer algorithms to execute trading strategies automatically in financial markets. In India, algo trading has gained significant popularity among traders due to its ability to execute trades with speed, accuracy, and efficiency. Essentially, algo trading involves the creation and implementation of predefined sets of rules and conditions that guide the buying and selling of financial instruments such as stocks, commodities, currencies, and derivatives. These algorithms analyse market data, including price movements, volume, and other relevant indicators, to identify trading opportunities and execute orders swiftly without human intervention.
Algo trading or algorithmic trading is the use of computer algorithms to execute trades with speed and efficiency. Algo trading strategies can vary widely depending on factors such as market conditions, asset classes, risk tolerance, and investment objectives. Some of the common trading strategies for algo trading are explained hereunder.
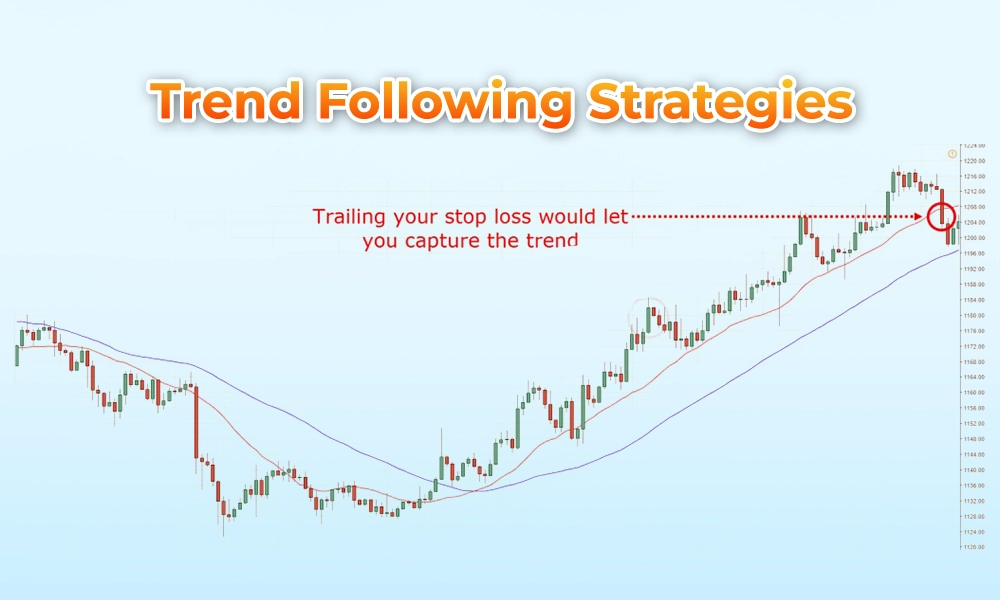
Trend-following strategies aim to capitalise on the momentum of an asset's price movement. These algorithms identify trends by analysing historical price data and technical indicators such as moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence). When a trend is identified, the algorithm may generate buy or sell signals to enter or exit positions in the direction of the trend.
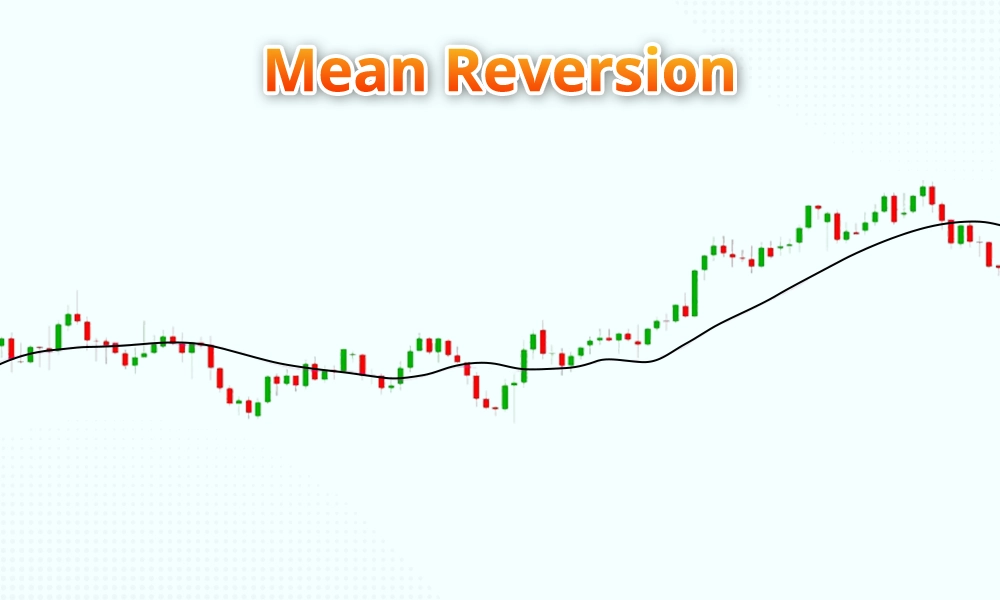
Mean reversion strategies operate on the principle that prices tend to revert to their historical average over time. These algorithms identify situations where an asset's price has deviated significantly from its historical mean and place trades betting on the price returning to its average level. mean reversion strategies may involve identifying overbought or oversold conditions using indicators such as Bollinger Bands or Stochastic Oscillator and executing trades accordingly.
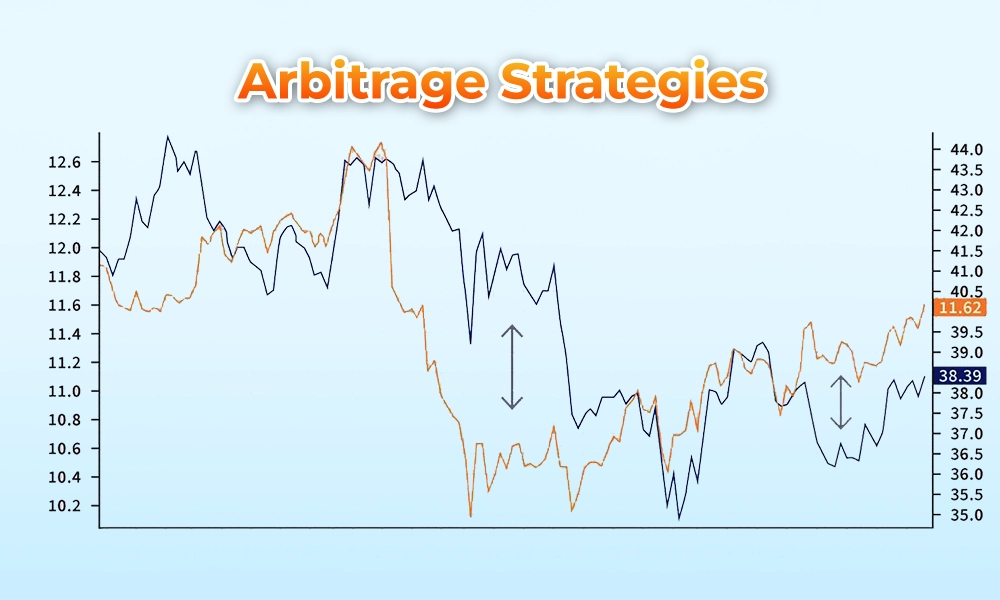
Arbitrage strategies seek to exploit price discrepancies between related assets or markets. These opportunities may arise between different stock exchanges, between the cash and futures markets, or between stocks and their derivatives. Algo trading algorithms scan multiple markets simultaneously, looking for price differentials that can be exploited for risk-free profit. High-Frequency Trading (HFT) firms often employ arbitrage strategies due to their ability to execute trades at lightning-fast speeds.
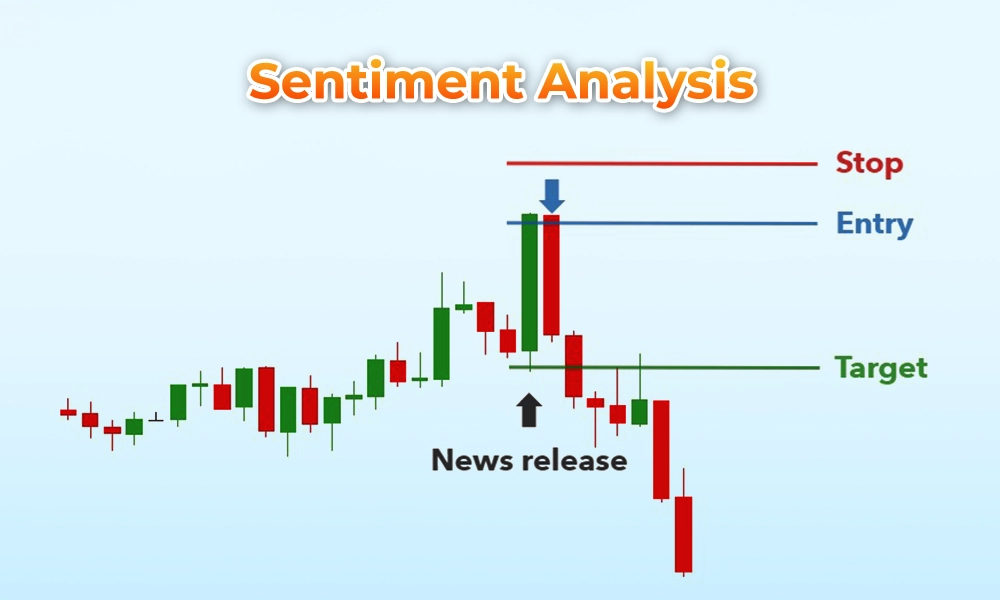
Sentiment analysis strategies aim to gauge market sentiment by analysing news articles, social media feeds, and other sources of information. These algorithms use natural language processing (NLP) techniques to extract sentiment-related signals and incorporate them into trading decisions. sentiment analysis strategies may focus on tracking news headlines, corporate announcements, and social media discussions to anticipate market movements and adjust trading positions accordingly.
Market making strategies involve providing liquidity to the market by continuously quoting buy and sell prices for a particular asset. Market making algorithms adjust their quotes dynamically based on factors such as order flow, volatility, and inventory levels to manage risk and capture spreads. Market making strategies are commonly used in equity and derivative markets, where liquidity provision is essential for efficient price discovery and order execution.
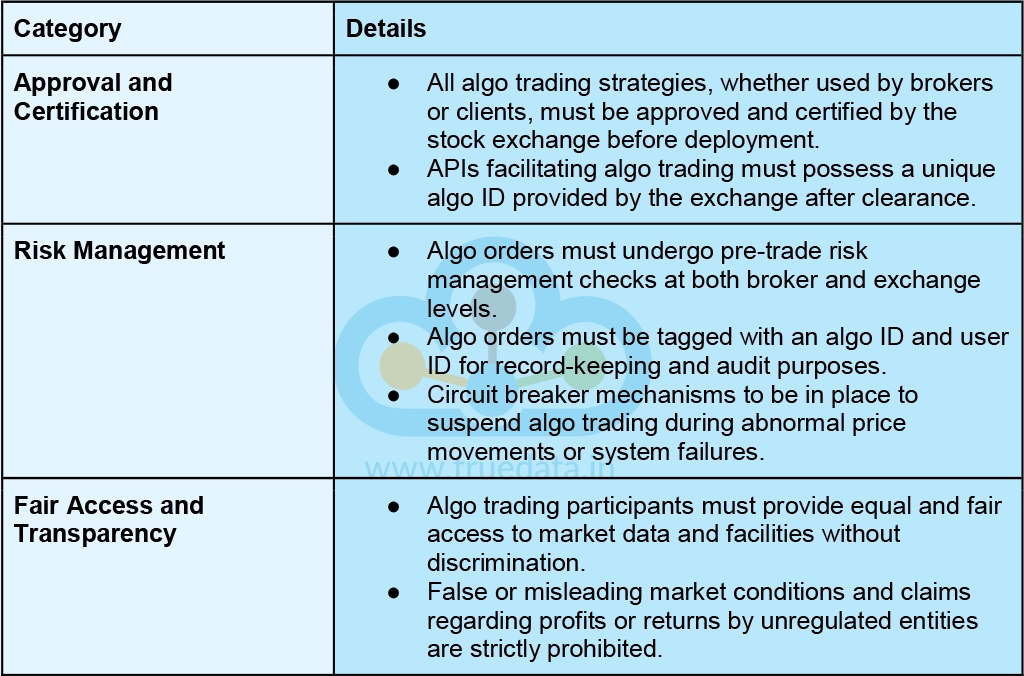
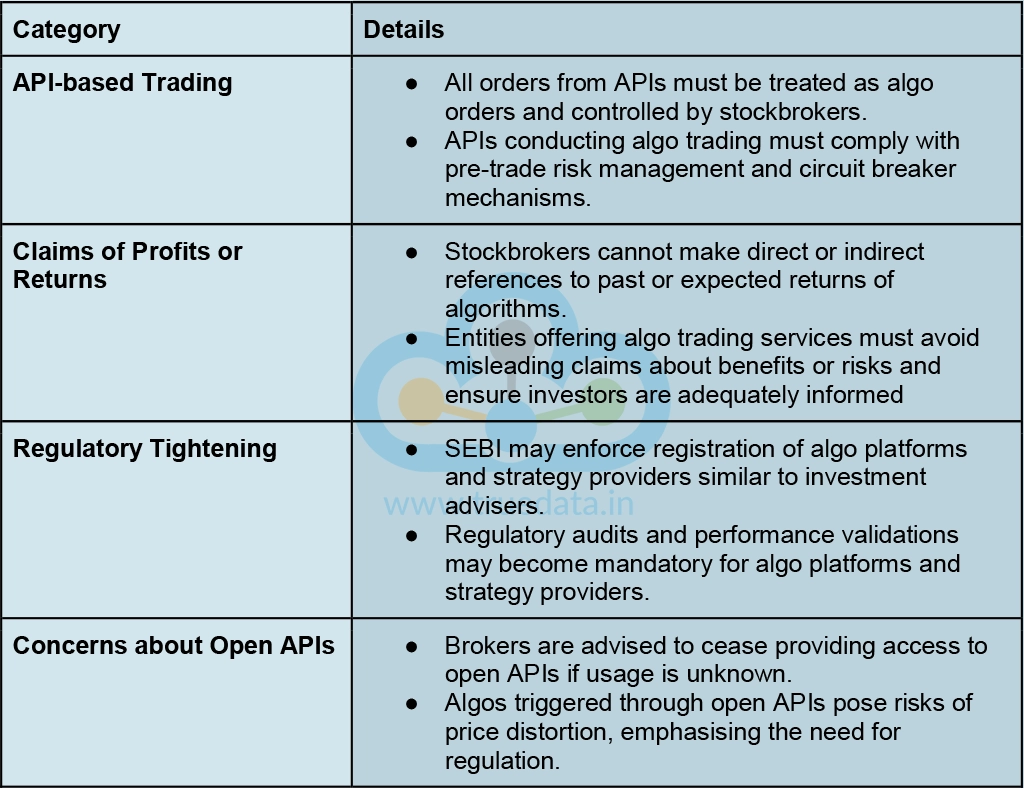
SEBI's guidelines and proposed changes aim to regulate algo trading, ensure transparency, and protect investor interests in India's financial markets. Some of the guidelines issued by SEBI in this regard are highlighted below.
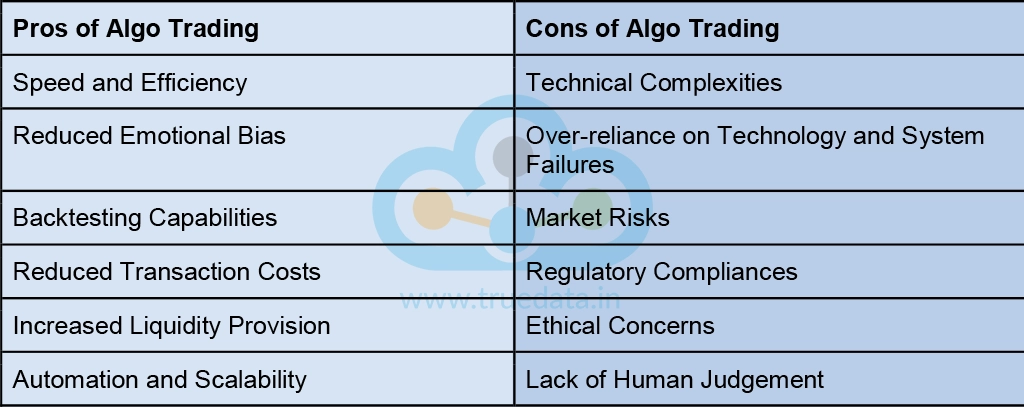
In order to execute algo trading and algo trading strategies successfully, one must also know the pros and cons of algo trading. A few prominent pros and cons of algo trading are highlighted hereunder.
Algo trading is fast-paced trading that is more or less in line with the fast-paced life of the youth today. The technology-driven approach of this trading allows better access and learning to the traders whether they are beginners in stock markets or seasoned players. Traders can leverage algorithmic trading to automate their strategies, increase trading efficiency, and potentially generate higher returns in the dynamic and competitive Indian financial markets. However, it's essential to thoroughly backtest and validate algorithms before deploying them in live trading environments to ensure robustness and consistency in performance.
This article was a brief introduction to algo trading and its increasing presence among retail traders. Let us know if you need further details on this topic and we will address them.
Till then Happy Reading!
Read More: Exploring HFT (High Frequency Trading) - Risks and Rewards
In the world of high-speed trading, success often hinges on capitalising on even...
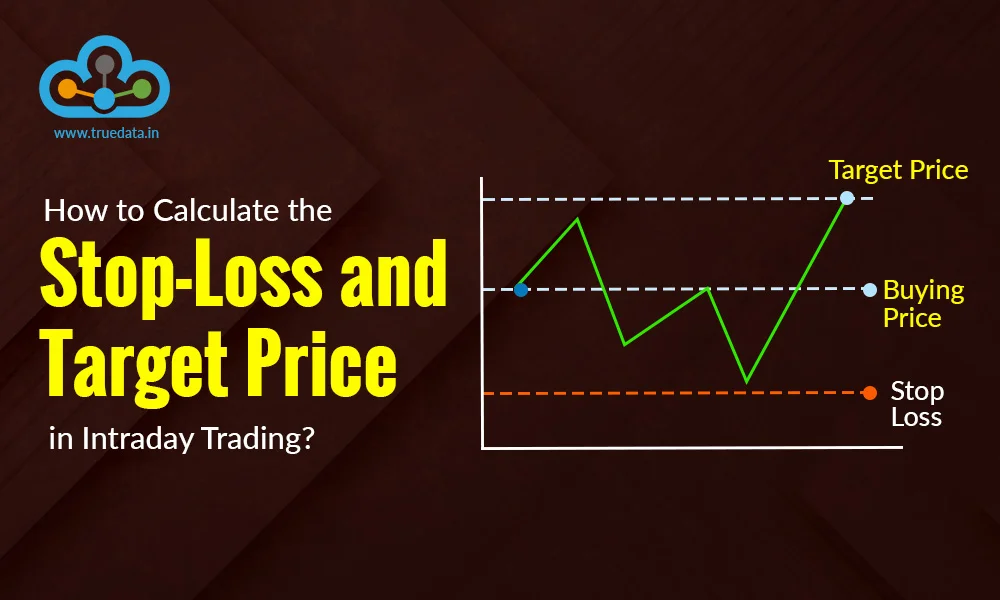
Did you know the number of intraday traders in India increased by over 300 from ...

The world of trading is constantly evolving with the use of advanced technology ...