
Stock market volatility can feel like a rollercoaster, with prices constantly moving due to many internal and external factors. One way investors make sense of this movement is by examining beta, a simple measure that helps you understand how sensitive a stock is to market swings. When you know a stock’s beta, you get a clearer picture of market sentiment and can make smarter entry and exit decisions. Curious to understand how beta works and why it matters for building a strong, balanced portfolio? Dive into this blog to explore everything about beta in the stock market.
Beta in the stock market indicates how much a stock moves in relation to the overall market, usually the Nifty 50. It helps investors understand whether a stock is riskier or more stable than the market. A beta of 1 means the stock moves in the same direction and at the same pace as the market. A beta greater than 1 means the stock is more volatile and tends to rise or fall faster than the market. A beta less than 1 indicates that the stock is more stable and shows smaller price movements. Beta indicates to an investor how sensitive a stock is to market fluctuations, helping them determine whether it fits their risk level and investment style.
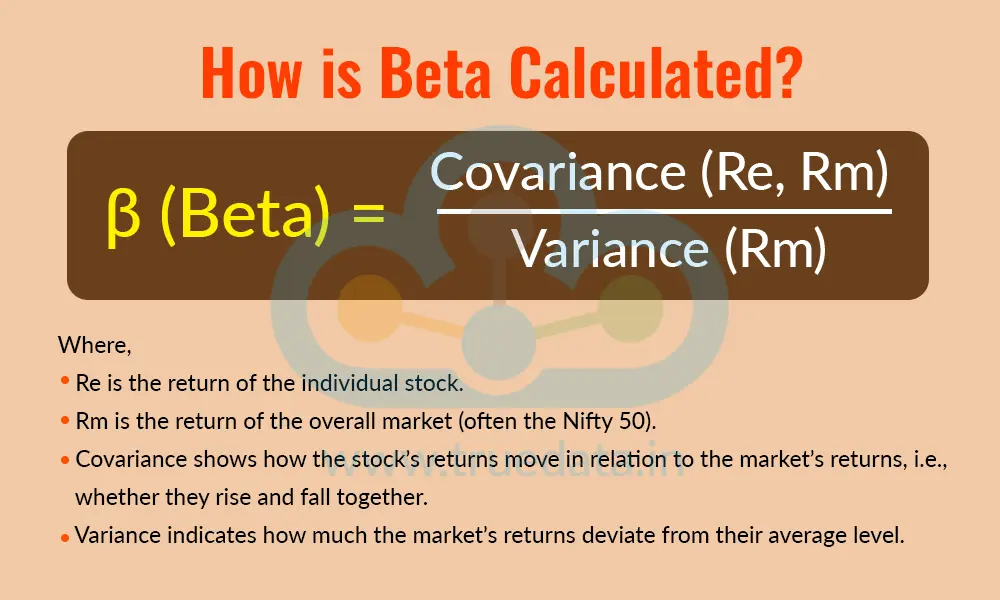
Beta is calculated by comparing a stock’s past price movements with the market’s past price movements over the same period. In simple terms, it measures how much the stock has moved relative to the market. Beta is calculated using a statistical formula that incorporates covariance (how the stock and market move together) and variance (how much the market fluctuates independently). However, for most investors, the idea is straightforward, i.e., if a stock usually rises or falls more than the market, its beta will be high. On the other hand, if it moves less, its beta will be low.
The formula to calculate Beta is,
β (Beta) = Covariance (Re, Rm) / Variance (Rm)
Where,
Re is the return of the individual stock.
Rm is the return of the overall market (often the Nifty 50).
Covariance shows how the stock’s returns move in relation to the market’s returns, i.e., whether they rise and fall together.
Variance indicates how much the market’s returns deviate from their average level.
To put it simply, beta measures how closely a stock follows the market and how strongly it reacts to market movements. Covariance captures the relationship between the stock and the market, while variance measures the market’s own movement. The beta derived from this formula shows the stock’s sensitivity compared to the market.
Let us understand the use and interpretation of beta using a simple example.
Consider investor A who compares a stock with the Nifty 50 Index over a few months. Whenever the Nifty 50 moves 1%, the stock typically moves about 1.5% indicating the stock reacts more strongly to market changes. So its beta will be around 1.5, suggesting the stock is 50% more volatile than the market. On the other hand, if the stock moves only 0.7% when the Nifty 50 moves 1%, its beta would be approximately 0.7, indicating that it is more stable and less sensitive to market swings.
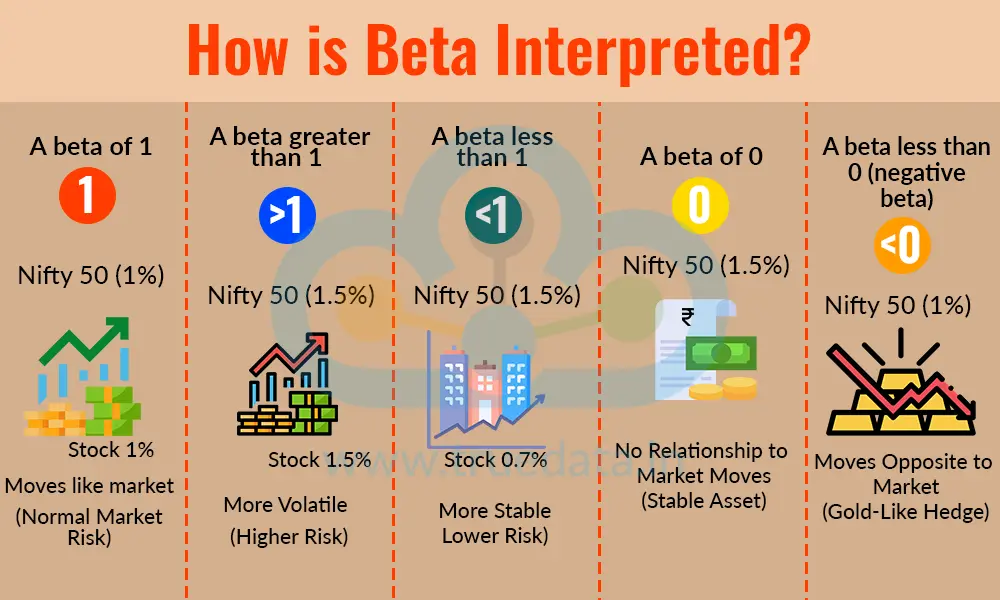
Beta of the stock market helps investors understand how much market risk a stock carries and whether it matches their risk tolerance, investment goals, and trading style. The interpretation of this beta is explained below.
A beta of 1 - When a stock has a beta of 1, it generally moves in the same direction and by the same percentage as the market. If the Nifty 50 rises 1%, this stock is likely to increase around 1% as well. It carries normal market risk and behaves much like the overall market.
A beta greater than 1 - A beta greater than 1 means the stock is more volatile than the market. For example, with a beta of 1.5, the stock may move 1.5% when the market moves 1%. Such stocks offer higher return potential during market upswings but can also decline more rapidly during downturns. They suit investors who are comfortable with higher risk.
A beta less than 1 - A beta less than 1 indicates a more stable stock that reacts less to market changes. For example, a beta of 0.7 means the stock moves only 0.7% when the market moves 1%. These stocks are typically from stable sectors and are preferred by conservative investors looking for stability.
A beta of 0 - A stock or asset with a beta of 0 has no relationship with market movements. This means its price does not rise or fall because of market changes. Some examples in this case include certain debt instruments or money market products. A beta of 0 indicates the asset adds stability to a portfolio and helps reduce overall market-driven risk.
A beta less than 0 (negative beta) - A negative beta means the stock moves in the opposite direction of the market. If the market rises, the stock may go down, and vice versa. Although this is rare, gold-like assets sometimes show such behaviour. These can act as hedges, offering protection when equity markets fall.
Beta can be used to determine stock volatility, thereby helping investors select stocks that align with investors’ risk and investment goals. This measure enables the classification of stocks into high-beta and low-beta stocks. The meaning of these terms is explained below.
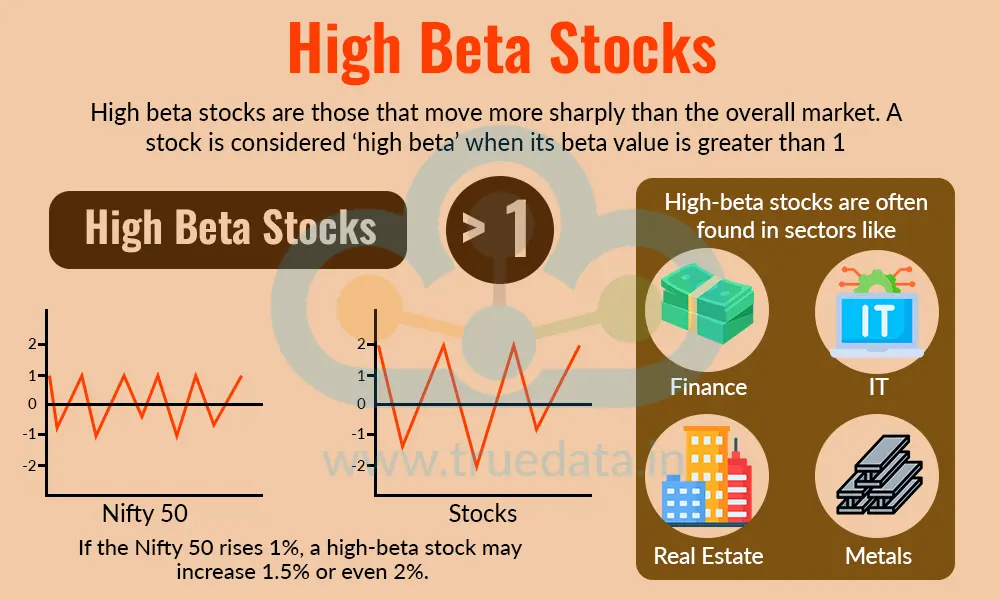
High beta stocks are those that move more sharply than the overall market. A stock is considered ‘high beta’ when its beta value is greater than 1. This means the stock reacts strongly to changes in the market. For example, if the Nifty 50 rises 1%, a high-beta stock may increase 1.5% or even 2%. Similarly, if the market falls, the stock may drop even more. High-beta stocks are often found in sectors like finance, IT, real estate, and metals in India, where prices tend to be more sensitive to economic news and market sentiment. These stocks can offer higher returns during market rallies but also carry higher risk during downturns. High-beta stocks are suitable for investors who are comfortable with volatility and seek faster growth opportunities.
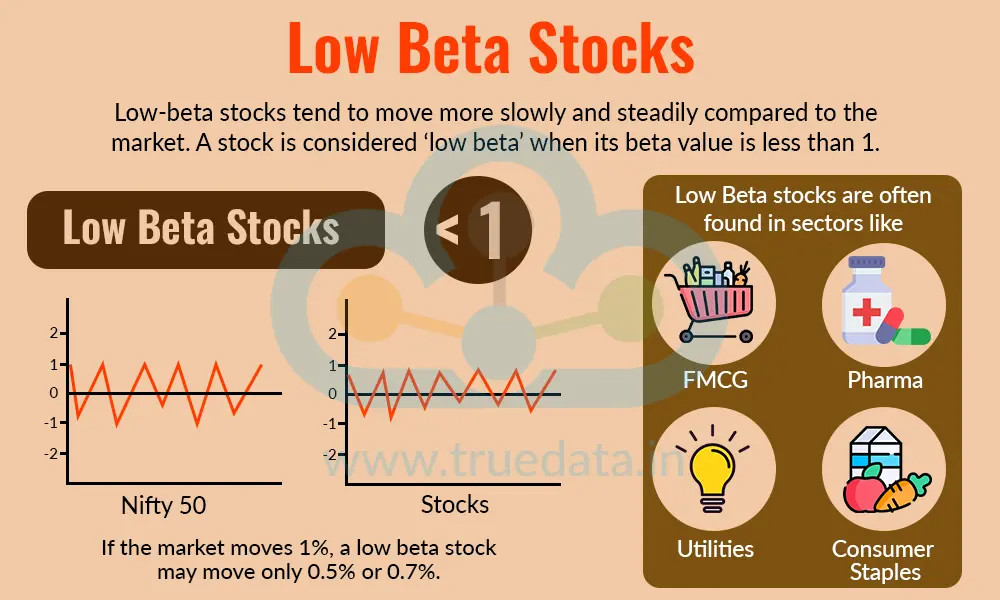
Low-beta stocks tend to move more slowly and steadily compared to the market. A stock is considered ‘low beta’ when its beta value is less than 1. This means the stock is less susceptible to market fluctuations. For example, if the market moves 1%, a low beta stock may move only 0.5% or 0.7%. Low beta stocks are usually from defensive sectors in India, like FMCG, pharma, utilities, and consumer staples, i.e., sectors where demand remains stable regardless of economic conditions. These stocks are preferred by conservative investors who want safety, steady returns, and lower volatility. Low beta stocks help reduce overall portfolio risk and provide stability during times of market uncertainty.
Apart from the beta, the other crucial term for investors to focus on is the alpha in the stock market.
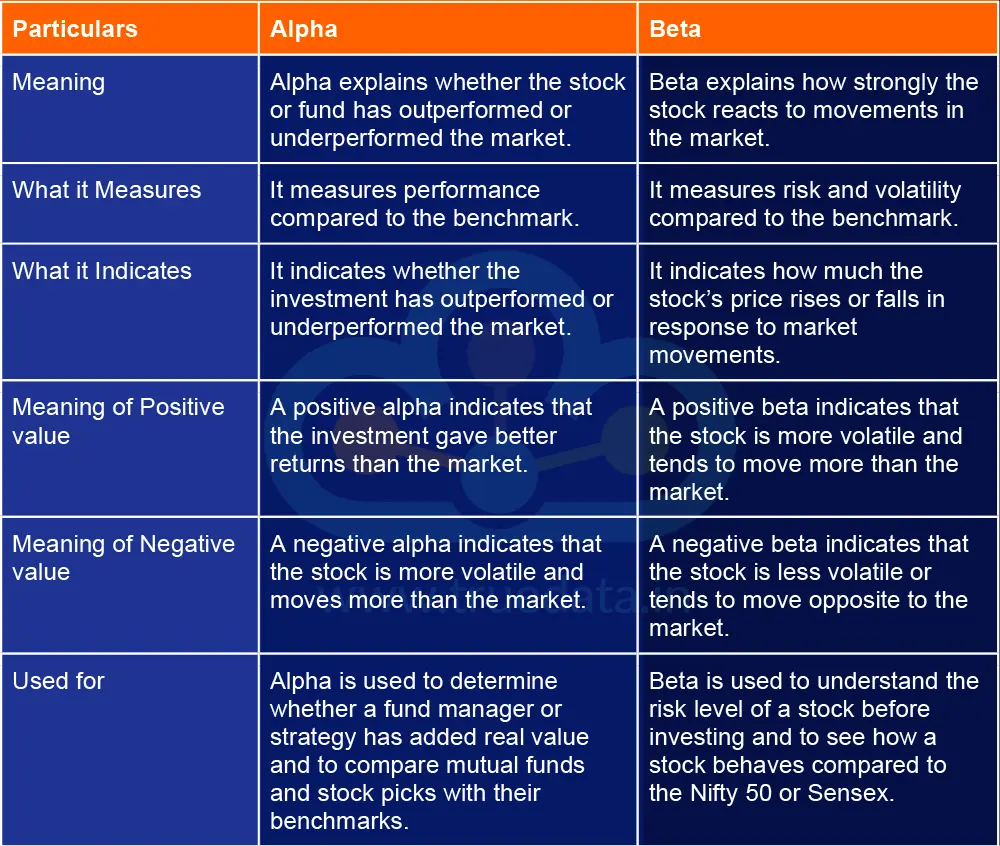
The Alpha tells an investor how much extra return a stock or fund has earned compared to the overall market. If the alpha is positive, it means the investment has outperformed the market. If the alpha is negative, it means the investment has done worse. Alpha helps investors understand whether the strategy or fund manager has added value.
Beta, on the other hand, shows how much a stock’s price changes compared to the market. A high beta indicates that the stock moves more than the market and is more volatile. A low beta means the stock moves less and is more stable. Beta helps investors judge the amount of market-related risk in a stock.
The differences between alpha and beta in the stock market are explained below.
Beta is a helpful tool for investors to understand how sensitive a stock is to market movements and the level of risk it carries compared to the overall market. By understanding the beta of a stock, an investor can assess its volatility, stability, and behaviour during market ups and downs. When used in conjunction with concepts like alpha and basic market analysis, beta helps investors choose stocks that match their risk level and build a more balanced and confident portfolio.
This article sheds light on key market terms and how they can be used to create a successful portfolio. Let us know your thoughts on this topic or if you need further information on the same, and we will address it soon.
Till then, Happy Reading!
Read More: How to Calculate Stop Loss Target Price in Intraday Trading?

The year 2023 began with a bummer for the Indian stock markets which saw a sign...

July 2023 marked a new era in theIndian stock markets with the addition of GIFT ...
Introduction Real Time Data from NSE, BSE & MCX is distributed to various d...