When it comes to judging how well a company is really performing, two numbers often steal the spotlight, i.e., ROE (Return on Equity) and ROCE (Return on Capital Employed). There are dozens of profitability ratios out there, each telling its own version of the story. However, what matters for investors is quite simple, i.e., ‘how much return am I actually getting on my money?’ That is where ROE and ROCE shine. The tricky part, though, is knowing which one to look at and when. The answers lie in this post, where we break down what each ratio means, their differences and how you can use them to make smarter investment calls.
Return on Equity (ROE) is a simple yet powerful ratio that tells an investor how efficiently a company is using the money invested by its shareholders to generate profits. In plain terms, it shows how much profit the company makes for every rupee of shareholder equity. For example, if a company has an ROE of 15%, it means the business earns Rs. 15 in profit for every Rs. 100 that shareholders have invested. Investors often use this measure to compare companies within the same sector, because it highlights which business is delivering stronger returns on the owners’ capital. A consistently high ROE suggests that the company has good management, strong business practices, and the ability to reinvest profits effectively. However, investors should also be cautious, as sometimes a high ROE can come from excessive debt, not just efficient operations. Therefore, while ROE is an important starting point, it should always be considered along with other factors before making an investment decision.
ROE is the return that shareholders expect on their investment. It is the ratio of two crucial elements, i.e., the net profit and the total shareholders’ equity.
The common formulas for calculating the ROE are provided below.
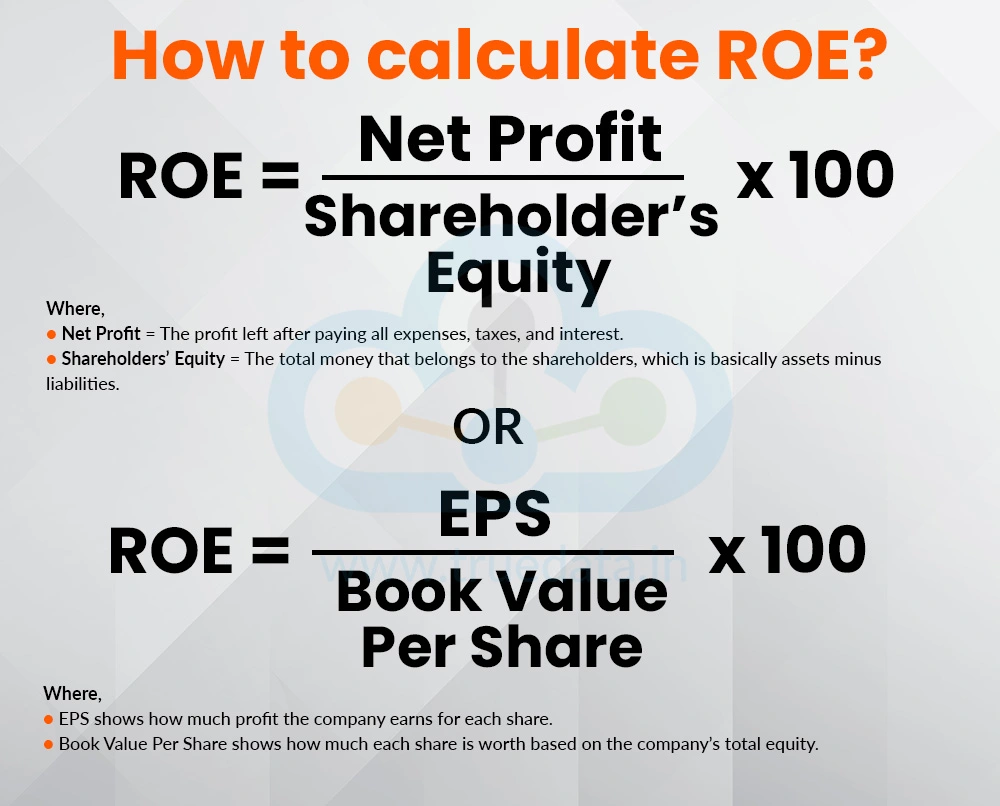
ROE = (Net Profit / Shareholders’ Equity) * 100
Where,
Net Profit = The profit left after paying all expenses, taxes, and interest.
Shareholders’ Equity = The total money that belongs to the shareholders, i.e., assets minus liabilities.
OR
ROE = EPS / Book Value Per Share * 100
This formula tells how much return a company is generating for each rupee of shareholders’ equity, on a per-share basis.
Where,
EPS shows how much profit the company earns for each share.
Book Value Per Share shows how much each share is worth based on the company’s total equity.
Understanding The Calculation of ROE With an Example
Consider Company XYZ Ltd. with a net profit of Rs. 50 crores and shareholders’ equity of Rs. 250 crores. The ROE of the company will be,
ROE = (50 / 250) * 100 = 20%
This means the company generated a 20% return on the money that shareholders invested. In other words, for every Rs. 100 of equity, the company earned Rs. 20 in profit. Investors usually prefer a company with a consistently high ROE, as it indicates the company is putting shareholders’ money to good use. Therefore, it is essential to compare the company's ROE with that of its previous years and its peers in the industry.
Consider Company ABC Ltd. with EPS of Rs. 8 and Book Value Per Share of Rs. 40. The ROE of the company based on this data will be,
ROE = EPS / Book Value Per Share * 100
ROE = 8/10*100 = 20%
This means the company earns a 20% return on the equity invested per share, or for every Rs. 100 of shareholders’ equity, the company generates Rs. 20 in profit.
ROE is important for both companies and investors. It helps in understanding the performance of the company as well as its growth potential.
The Importance of ROE for Companies -
Return on Equity (ROE) is often seen as a report card for a company’s management. It shows how effectively the company is using shareholders’ money to generate profits. A high and consistent ROE indicates the management team is making the right decisions and running the business efficiently. On the other hand, a weak ROE can be an early warning sign that capital is not being used in the best possible way.
Most industries in our country, whether it is banking, IT, FMCG, or automobiles, are highly competitive. Companies are constantly trying to capture market share and improve margins. In such an environment, a consistently strong ROE helps a company stand apart. It tells investors that the business model works well even when competition is tough, which builds long-term confidence in the company.
A higher ROE is a positive sign because it means the company is not just making profits but also reinvesting them wisely to create more value for its shareholders. For example, if a company earns Rs. 20 on every Rs. 100 of shareholder equity, that is money being put to productive use. Over time, this reinvestment helps the company grow faster and rewards shareholders with better returns.
Companies with healthy ROE figures usually find it easier to attract new investors or raise funds from banks and institutions. This is because they already have a proven track record of turning capital into profits. For potential investors, a strong ROE serves as evidence that their money will be used effectively, reducing the risk of investment.
Another reason why ROE is important is that it highlights whether the company’s business model is scalable. A scalable model means the company can grow revenues and profits without proportionally increasing costs. If ROE remains strong as the business expands, it shows that management strategies and operations can support long-term growth.
The Importance of ROE for Investors -
Return on Equity (ROE) is one of the simplest ways to see how much profit a company is generating from its invested capital. By looking at ROE, investors can understand whether the business is efficiently using shareholders’ funds to create profits.
A consistently high ROE indicates that the company can generate attractive returns without constantly needing additional capital. This is important for investors because it shows that the company can grow steadily while relying on the funds already invested by shareholders. Over time, this consistent performance can lead to better wealth creation for long-term investors.
While a high ROE is generally positive, investors need to be careful. A company may often show a high ROE not because it is genuinely profitable, but because it has taken on too much debt. High debt can artificially inflate ROE, which increases risk. Therefore, ROE should be considered along with other financial indicators to ensure that the returns are sustainable and not risky.
ROE is a reliable tool for investors, but it should not be the sole factor in making investment decisions. It provides a clear picture of how effectively a company is using shareholder funds, but it works best when combined with other metrics, such as debt levels, profit margins, and cash flow. This balanced approach helps investors make smarter, safer investment choices.

Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) is a financial ratio that shows how efficiently a company is using all the total capital available to it, which includes both shareholders’ equity and borrowed funds, to generate profits. Unlike ROE, which focuses only on shareholders’ money, ROCE gives a broader picture by including debt as well. This makes it especially useful in India, where many companies rely on loans to fund their growth. ROCE is calculated by dividing a company’s Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT) by the Capital Employed (which is total assets minus current liabilities). A higher ROCE means the company is putting its total capital to productive use and generating good returns from it. A consistently strong ROCE suggests that the business is not just profitable but also efficient in managing both debt and equity. This makes it a valuable tool for comparing companies in capital-intensive sectors like infrastructure, manufacturing, and power, where borrowed money plays a big role in business operations.

ROCE is the measure of the ability of the company to generate returns from the total capital employed by the company. The calculator of ROCE includes the use of two important parameters from the company’s financial statements, i.e., the EBIT and the total capital employed.
The formula to calculate ROCE is,
ROCE = (Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT) / Capital Employed) * 100
Where,
Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT) = This is the company’s operating profit before paying interest and taxes. It shows profit from core business activities.
Capital Employed = This is the total long-term funds used in the business. It is usually calculated as Total Assets - Current Liabilities, or simply as Equity + Debt.
Understanding The Calculation of ROCE With an Example
Consider Company ABC Ltd., having an EBIT of Rs. 40 crore and capital employed of Rs. 200 crore (includes shareholders’ equity and long-term debt). The ROCE for ABC Ltd. will be calculated as follows.
ROCE = (Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT) / Capital Employed) * 100
ROCE = (40/200) * 100 = 20%
This means the company is generating a 20% return on the total capital employed. In simple words, for every Rs. 100 invested in the business (from both shareholders and lenders), the company earns Rs. 20 in operating profit.
ROCE is an effective tool to understand the operational efficiency as well as the management efficiency for effective capital deployment. Thus, it becomes an important metric for fundamental analysis of a company.
Importance of ROCE for Companies -
Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) acts as an important tool to check how efficiently they are using all the funds available (both shareholders’ money and borrowed money). A strong ROCE indicates that the company is not just generating profits, but also making the most out of every rupee invested in the business. This helps management understand whether their strategies and operations are truly effective.
Many businesses in India, such as infrastructure, manufacturing, telecom, and power, depend heavily on borrowed funds to expand and run their operations. For such companies, ROCE becomes especially important because it shows whether the borrowed money is being used productively. A higher ROCE suggests that the company is able to generate strong returns despite carrying large amounts of debt, which reflects disciplined and efficient financial management.
Another major advantage of maintaining a strong ROCE is that it boosts the company’s credibility in the eyes of banks, financial institutions, and investors. When a business demonstrates the ability to generate good returns on capital, it becomes easier for it to raise fresh funds for expansion or new projects. This trust factor can make a big difference in gaining access to low-cost loans and attracting more investor interest.
Importance of ROCE for Investors -
ROCE helps investors evaluate the company in a better and refined manner by looking beyond the traditional profits or just the ROE. ROCE helps in understanding the value generated for both shareholders and lenders. In simple words, it shows how effectively the company is using all the money it has to generate profits. This makes ROCE a more complete measure of financial efficiency.
Using ROCE helps investors to make more informed decisions about where their money is likely to grow faster and safer. A company with consistently high ROCE shows disciplined capital management, which reduces investment risk. This makes ROCE an essential metric for long-term investors to consider alongside other financial indicators before committing funds.
Many companies in India operate with significant borrowings as they expand in a competitive market. For investors, ROCE becomes a reliable tool to judge which company is putting its capital to better use. For example, when comparing two infrastructure firms, the one with the higher ROCE is usually more efficient in handling debt and equity together. This comparison helps investors pick stronger businesses in the same sector.
ROE and ROCE are two sides of the same coin that involve ascertaining the net returns available to the stakeholders. However, they cater to different sets of users and provide different insights. The difference between ROE and ROCE is explained hereunder.
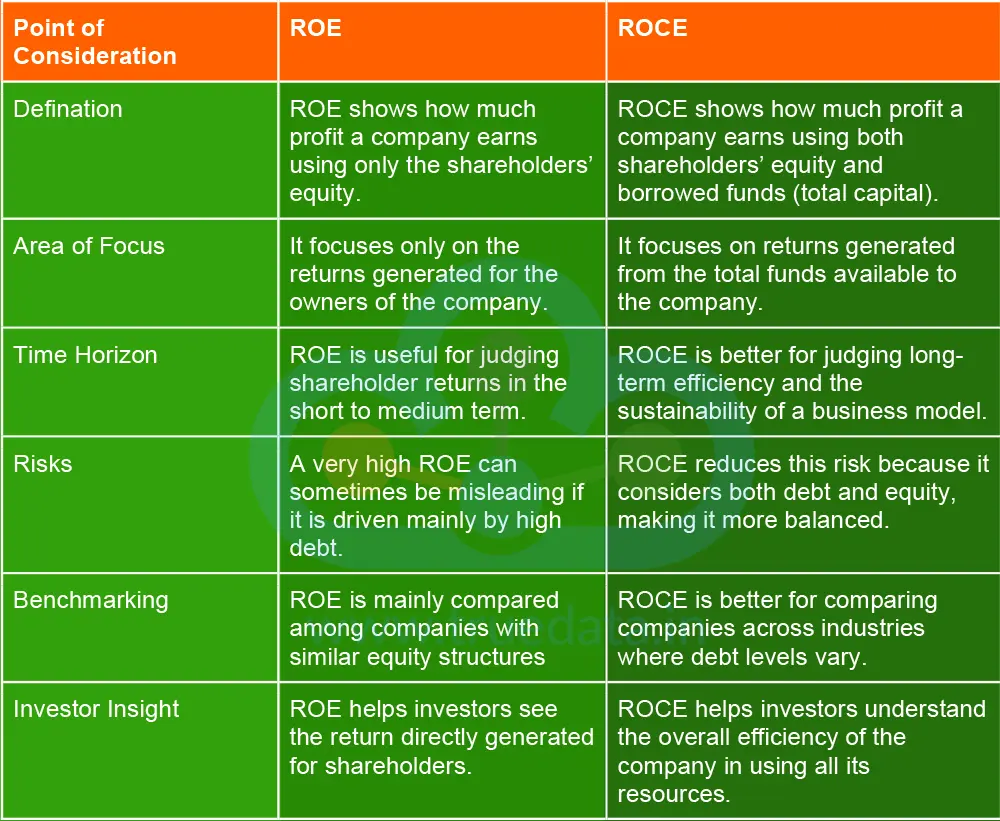
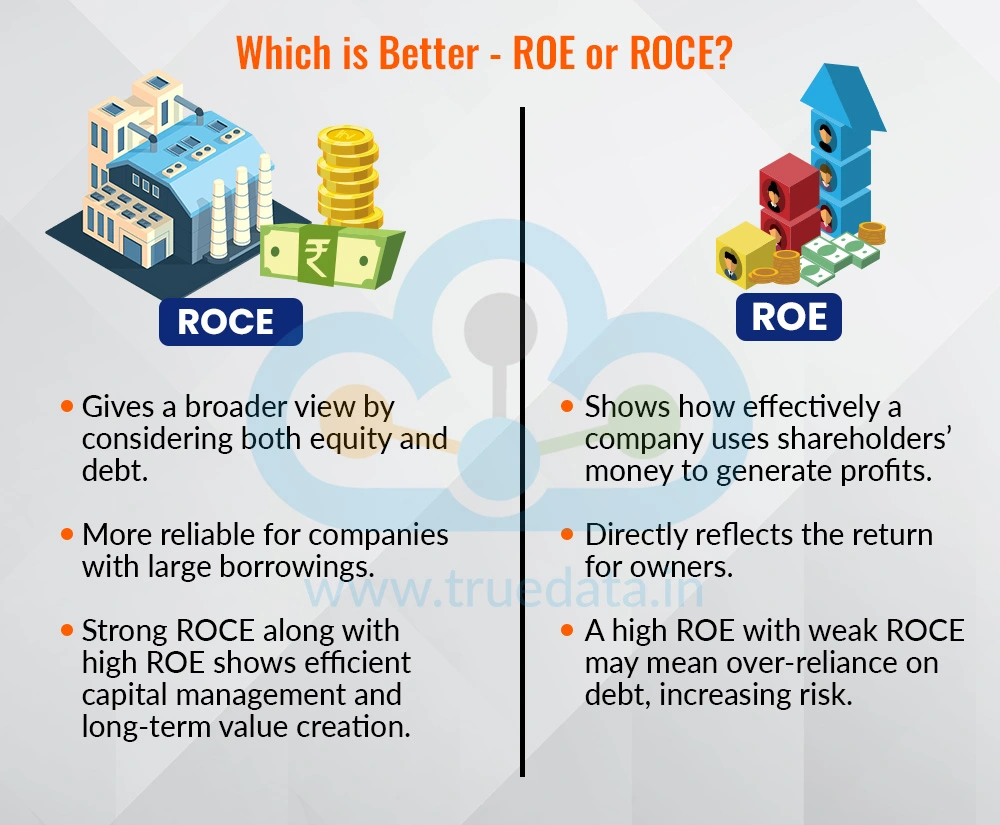
There is no standard answer to this question as each tells a different part of the story. ROE is useful for investors who want to know how effectively a company is using shareholders’ money to generate profits. It directly reflects the return for owners. On the other hand, ROCE gives a broader view because it looks at both equity and debt, making it more reliable for companies that use large borrowings. Thus, investors should not rely on one metric and look at both ROE and ROCE together. A company with a high ROE but weak ROCE may be relying too much on debt, which increases risk. A company with strong performance in both ratios is usually managing its capital efficiently and creating long-term value. Therefore, a smarter approach is to use ROE and ROCE side by side rather than choosing one over the other.
Analysing ROE and ROCE is part of the fundamental analysis of stocks and a crucial part of the process to evaluate the possible growth and sustainability of a company. While ROE is instrumental in understanding the net return per rupee for the shareholders, it is a narrower approach when analysing the company as a whole. Thus, for accurate analysis of a company’s efficiency and ability to generate return, it is important to use ROE and ROCE in combination with other metrics of fundamental analysis to get a complete picture.
This post talks about a significant step in company analysis and its ultimate impact on a portfolio. Let us know your thoughts on this topic or if you need any further information on the same, and we will address them.
Till then, Happy Reading!

Thestock market never stands still, and prices swing constantly with every new h...

Imagine a business without any competition. What's the outcome? An unchecked mon...

If you are a shareholder of a company, you would have seen its annual reports co...