
Imagine a business without any competition. What's the outcome? An unchecked monopoly resulting in the exploitation of consumers. Competition in any industry is the challenge that ensures that the ultimate winner is always the consumer. However, is it important for companies to understand their competition? The answer is absolutely yes! The best way to do that is through Porter’s Five Forces model. Curious to know more about it? Check out this blog to learn all about Porter’s Five Forces Model and how to use it for optimum competition analysis.
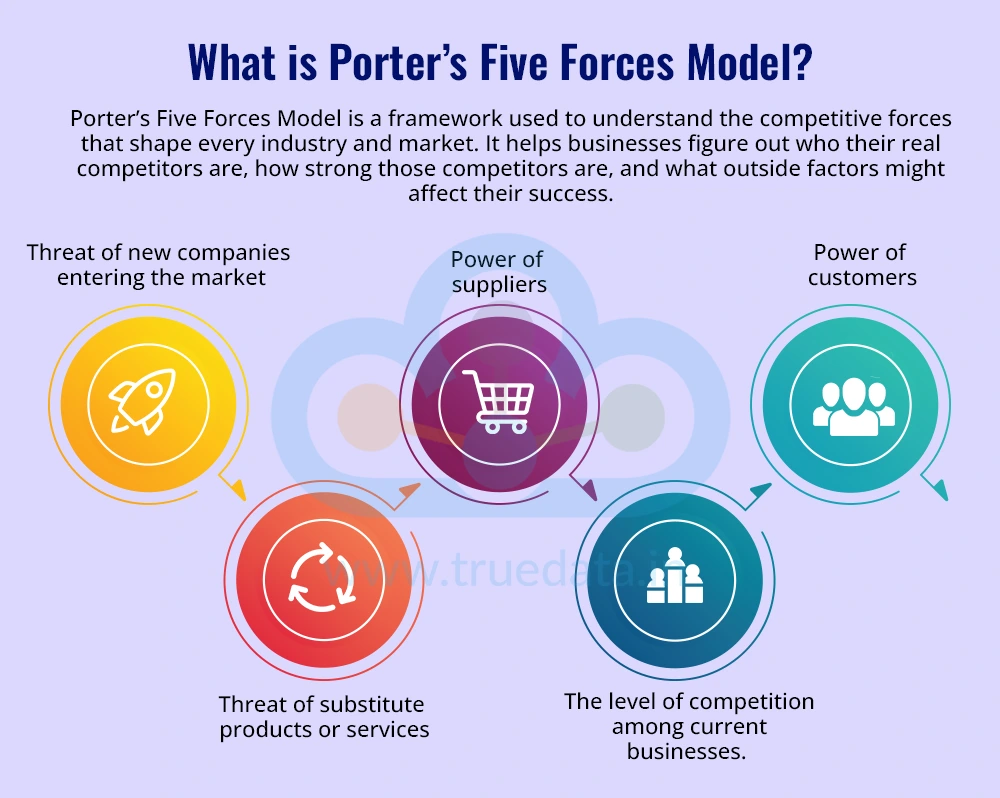
Porter’s Five Forces Model is a framework used to understand the competitive forces that shape every industry and market. It helps businesses identify their true competitors, assess their strengths, and understand the external factors that may impact their success. This model was introduced in 1979 by Michael E. Porter, a professor at Harvard Business School, in his book ‘Competitive Strategy’. His goal was to help businesses look beyond their immediate rivals and understand the bigger picture of what affects competition. Since then, Porter’s Five Forces has become one of the most widely used tools in business strategy around the world.
The model looks at five key areas, i.e.,
Threat of new companies entering the market
Power of suppliers
Power of customers
Threat of substitute products or services
The level of competition among current businesses.
Analysing these forces helps companies make smarter decisions about pricing, marketing, product development, and long-term strategy.
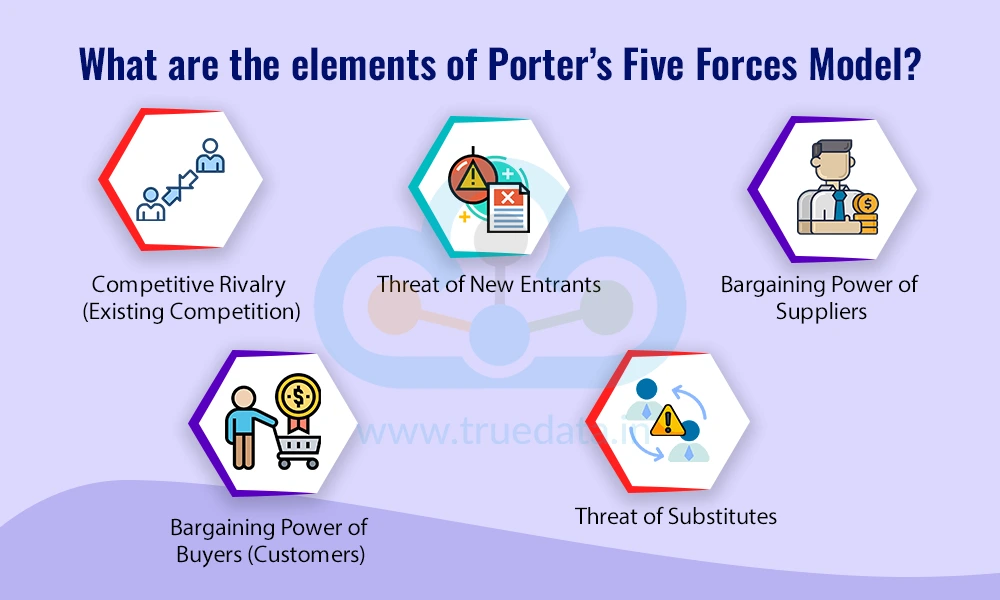
Porter’s Five Forces Model is a strategic tool that helps businesses understand the factors that affect competition in their industry. This model can be beneficial for companies in navigating dynamic markets, identifying opportunities, and managing threats. Here is a breakdown of these elements to help understand the model better.
This force examines the level of competition among existing businesses in the same industry. Markets like FMCG, food delivery, and e-commerce are highly competitive in a growing country like India. When many companies offer similar products or services, businesses must constantly improve quality, reduce costs, or offer something unique to attract and retain customers. A high level of rivalry can limit profit margins and market share.
This refers to how easily new players can enter a market and compete with established businesses. Sectors like online retail or education technology may have low entry barriers, making it easy for startups to emerge. However, industries like aviation or telecom require heavy investment, government approvals, and infrastructure, making entry more difficult. When entry is easy, existing companies face the risk of losing customers to new competitors.
Suppliers provide the raw materials or services needed for a business to operate. If there are only a few suppliers in the market, they hold more power and can demand higher prices or limit supply. For example, a manufacturer dependent on a single source for a specific component may have less negotiating power. On the other hand, if there are many suppliers, companies have the advantage of choosing the best deal.
This force evaluates how much influence customers have over pricing and quality. Indian consumers are often price-conscious and have access to many alternatives, especially in sectors like electronics, food, and personal care. If customers can easily switch to another brand or bargain for better deals, companies must work harder to meet expectations through value, service, and innovation.
Substitutes are alternative products or services that serve the same purpose. For example, public transport can be a substitute for private vehicle ownership. Similarly, traditional banking services face substitutes from fintech apps. When substitutes are available and affordable, they can take away customers and reduce a company's market share. Businesses must constantly innovate and differentiate their offerings to stay relevant.
Porter’s Five Forces Model is a valuable tool for companies, whether large corporations, small startups, or even individual entrepreneurs. This model can be used by companies at different stages of planning and decision-making. Here is a brief explanation for the same.
Before launching a new business, it is important to understand the market environment. Porter’s Five Forces helps identify how competitive the industry is, how easy it is for others to enter the same space, and how much control suppliers and customers have. For example, someone planning to open a café in Bengaluru can use this model to assess nearby competition, supplier options, customer expectations, and alternatives like food delivery apps. This analysis can guide smarter choices in location, pricing, and marketing.

Companies looking to expand into a different sector or state can use this model to evaluate potential risks and opportunities. For instance, a successful garment business in Delhi planning to enter the footwear market in Maharashtra should analyse factors like the threat of existing shoe brands, local suppliers, customer demand, and regional preferences. Porter’s model helps in understanding how tough it might be to survive and what strategies are needed.
Porter’s Five Forces can help pinpoint the reason if a company notices that its profits are declining or that customers are shifting to competitors. It can also be used to find answers to situations like a new player entering the market, customers demanding lower prices or better service or substitutes becoming more popular. This model helps companies take a deeper look at external pressures and respond with better strategies, such as improving products, revising prices, or focusing on customer loyalty.

Regular reviews of strategy are essential even for businesses that are already established. Indian markets are fast-changing with new competitors, technologies, and changing customer preferences. By using the Five Forces, companies can reassess their strengths and weaknesses for better analysis and strategy. For example, a traditional grocery store can analyse how online platforms like BigBasket or JioMart are changing customer behaviour and decide whether to go digital.
If a company is planning to merge with or acquire another business, Porter’s Five Forces can help assess the competitive health of the target company’s industry. For instance, if a pharmaceutical company in Hyderabad is acquiring a smaller drug manufacturer, they can evaluate how competitive the industry is, how much pricing control suppliers and customers have, and whether generic substitutes threaten future profits. This analysis helps in making smarter investment and negotiation decisions.

Indian companies planning to export products or enter foreign markets can use the Five Forces to understand competition abroad. For example, a food products company from Gujarat aiming to enter the Middle East market can use this model to study local competitors, customer preferences, legal barriers, and alternative products. This insight helps in creating a customised entry strategy for international success.

Supply disruptions can have a big impact on companies, especially in industries like agriculture, manufacturing, or textiles. Porter’s model helps assess the bargaining power of suppliers, i.e., if suppliers are few or located in unstable areas, they may raise prices or delay delivery. Understanding this helps businesses look for alternative suppliers, renegotiate contracts, or invest in local sourcing to reduce dependency.

Porter’s Five Forces Model can be used to analyse stocks for investment. The steps for the same include,
Choose a Company
Pick a listed company (e.g., Infosys, HDFC Bank, Tata Motors).
Study the Industry
Understand the sector (IT, Banking, FMCG, Auto, etc.).
Use business news, company reports, and sector overviews (from NSE/BSE).
Apply the Five Forces
Competitive Rivalry
Are there many strong competitors?
High rivalry indicates lower profits.
Example - FMCG has high rivalry (HUL vs. Dabur vs. ITC).
Threat of New Entrants
Is it easy for new players to enter?
Tough entry indicates safer profits for existing firms.
Example - Banking has high entry barriers in India.
Supplier Power
Are there a few suppliers that control prices?
More supplier power indicates less profit for the company.
Example - The Auto sector depends on parts suppliers.
Buyer Power
Can customers easily switch brands?
Strong buyers indicate more pressure on prices.
Example - Telecom users switch between Jio, Airtel, and Vi.
Threat of Substitutes
Are there other products customers can use instead?
More substitutes indicate more risk to profits.
Example - Online payments (UPI) reduce credit card usage.
Final Step - Decide Investment Potential
A company is stronger if,
It faces low threat from competitors, substitutes, and new entrants and has control over suppliers and buyers.
These factors suggest better future growth and safer investment.
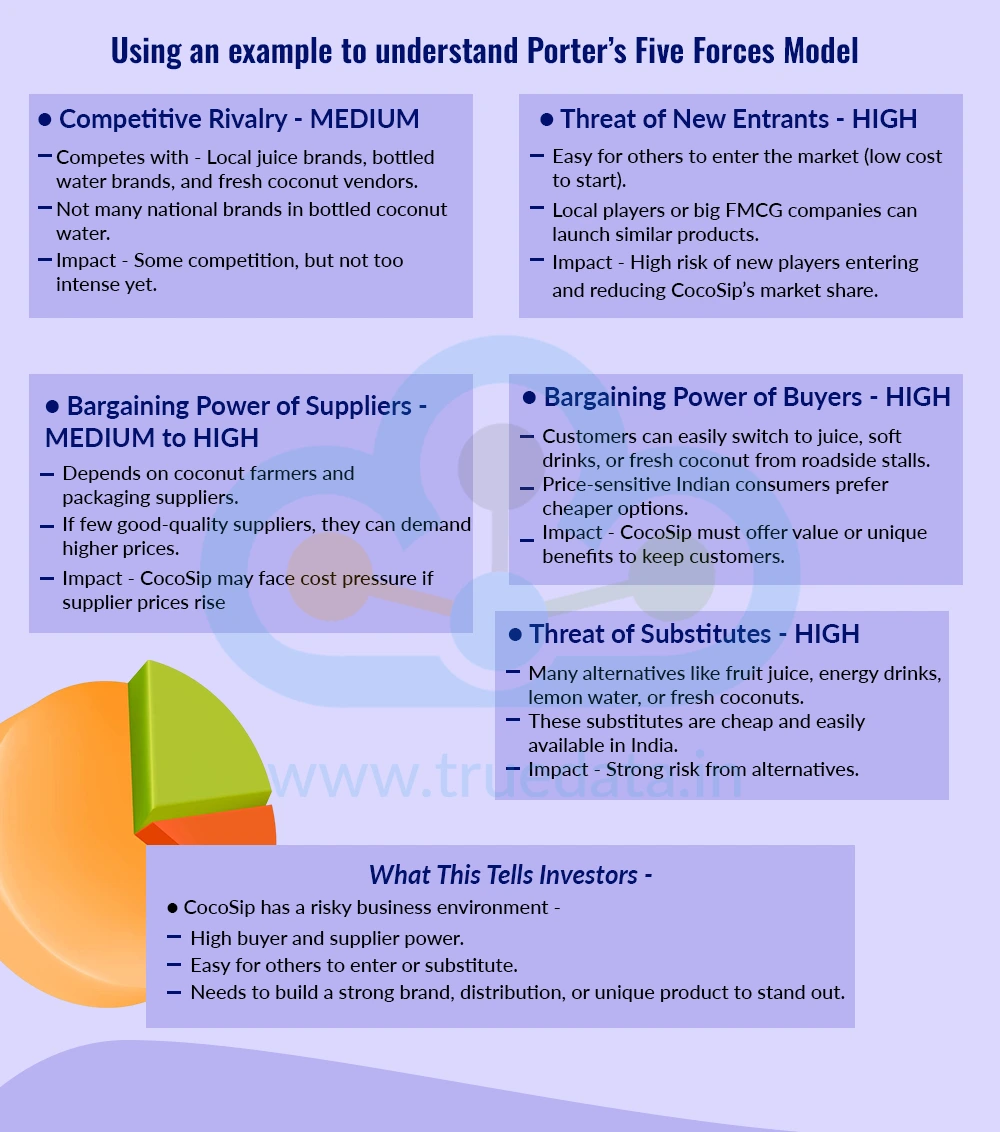
Let us understand the use of Porter’s Five Forces model with a hypothetical example.
Consider a startup venturing into a new market with their product ‘CocoSip’, which sells bottled coconut water in India. Porter’s Five Forces Model in this case will be applied as under.
Competitive Rivalry - MEDIUM
Competes with - Local juice brands, bottled water brands, and fresh coconut vendors.
Not many national brands in bottled coconut water.
Impact - Some competition, but not too intense yet.
Threat of New Entrants - HIGH
Easy for others to enter the market (low cost to start).
Local players or big FMCG companies can launch similar products.
Impact - High risk of new players entering and reducing CocoSip’s market share.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers - MEDIUM to HIGH
Depends on coconut farmers and packaging suppliers.
If few good-quality suppliers, they can demand higher prices.
Impact - CocoSip may face cost pressure if supplier prices rise.
Bargaining Power of Buyers - HIGH
Customers can easily switch to juice, soft drinks, or fresh coconut from roadside stalls.
Price-sensitive Indian consumers prefer cheaper options.
Impact - CocoSip must offer value or unique benefits to keep customers.
Threat of Substitutes - HIGH
Many alternatives like fruit juice, energy drinks, lemon water, or fresh coconuts.
These substitutes are cheap and easily available in India.
Impact - Strong risk from alternatives.
What This Tells Investors -
CocoSip has a risky business environment -
High buyer and supplier power.
Easy for others to enter or substitute.
Needs to build a strong brand, distribution, or unique product to stand out.
Investment is only good if the company shows strong growth, innovation, and a loyal customer base.
After understanding the Porter’s Five Forces Model and its importance in detail, let us now consider the pros and cons of using this model.
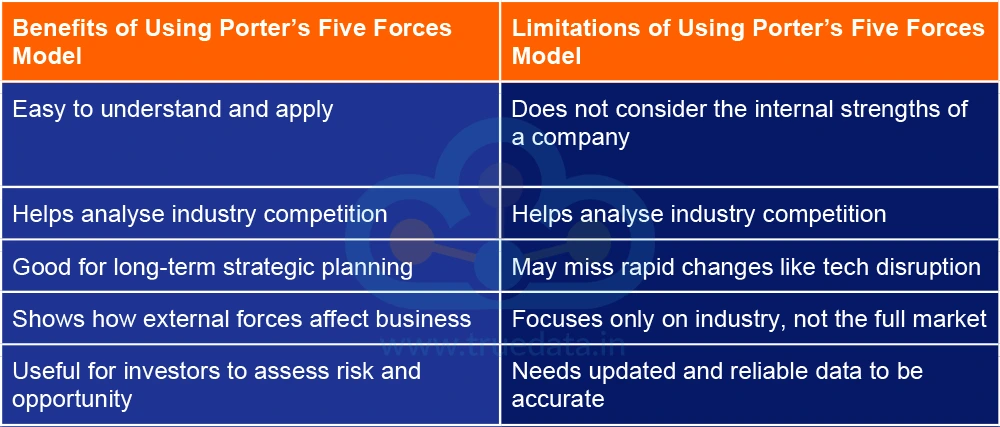
Porter’s Five Forces Model is a useful and easy tool for people and companies in India to understand how strong or risky an industry is before making business or investment decisions. While it helps in long-term planning and gives a clear view of industry challenges, it has some limits in its application. However, when used with other tools and an overall understanding of the business, Porter’s Five Forces Model can be a good starting point for smart business decisions or investment choices in the market.
This article deals with a specific area of fundamental analysis of stocks, i.e., competitor analysis. We hope you got useful insights from this topic. Let us know your thoughts or if you need further information on the same, and we will address it soon.
Till then, Happy Reading!
Read More: Corporate Governance and Its Influence on Stock Performance

Thestock market never stands still, and prices swing constantly with every new h...

Every company has a core group of people who believe in its vision from day one,...

If you are a shareholder of a company, you would have seen its annual reports co...