
The stock markets have a constant pull and push of buyers and sellers, driving the prices of assets. Traders take advantage of these price fluctuations to find profitable trading opportunities. This price swing, based on the demand and supply functions, shapes the bid ask spread. Have you heard about it? Explore this blog to discover all about this crucial aspect of trading and its key details.
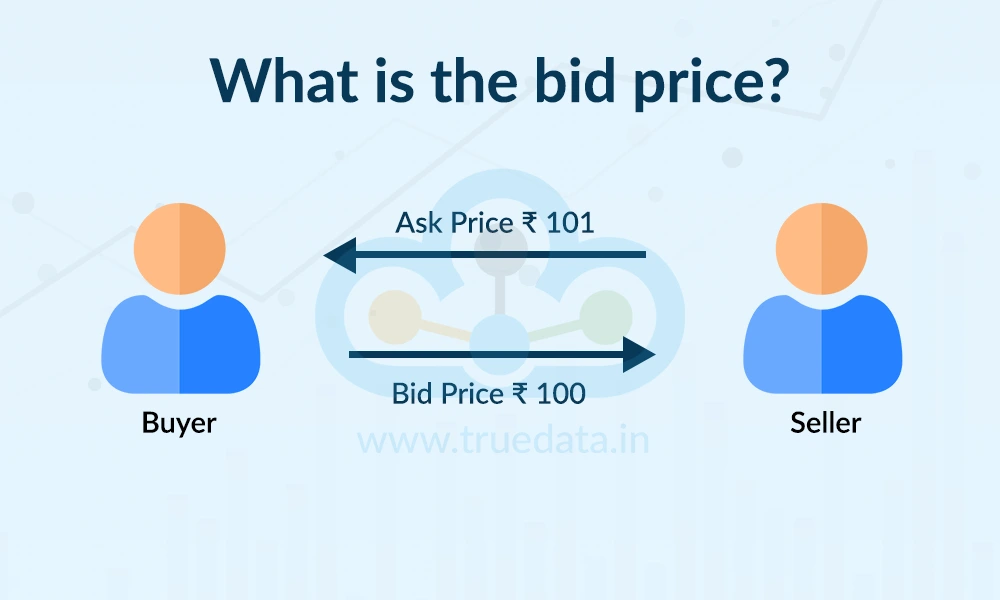
The bid price is the highest price that a buyer is willing to pay for a stock, commodity, or any financial asset at a given time. When traders place a buy order, the amount paid becomes the bid price. Other traders in the market can see this price and decide if they want to sell their shares to the trader at that rate. The bid price is important as it shows the current demand for a stock. If there are many buyers offering high bid prices, it means the stock is in demand.

The ask price (also called the offer price) is the lowest price at which a seller is willing to sell a stock, commodity, or any financial asset at a given time. When traders want to sell a share or an asset, the quoted price becomes the ask price. Other traders in the market can see this price and choose to buy from the trader if they agree with the rate. The ask price shows the supply side of the market. If many sellers are quoting lower ask prices, it means there is less demand or more supply.

The bid-ask spread is the difference between the bid price (the highest price a buyer is willing to pay) and the ask price (the lowest price a seller is willing to accept) for a stock or any financial asset. This spread shows how much of a gap there is between buyers and sellers. For example, if the bid price of a stock is Rs. 100 and the ask price is Rs. 101, the spread is Re. 1.
A smaller spread usually means that the stock is actively traded, with many buyers and sellers, which is called high liquidity. A larger spread means lower liquidity and can make it harder to enter or exit trades at a good price. The spread also affects trading cost as traders buying at the ask and selling at the bid lose the spread amount, so tighter spreads are better for frequent traders. In simple terms, the bid-ask spread tells traders how easy and cheap it is to trade a stock, and understanding it helps traders make smarter decisions.
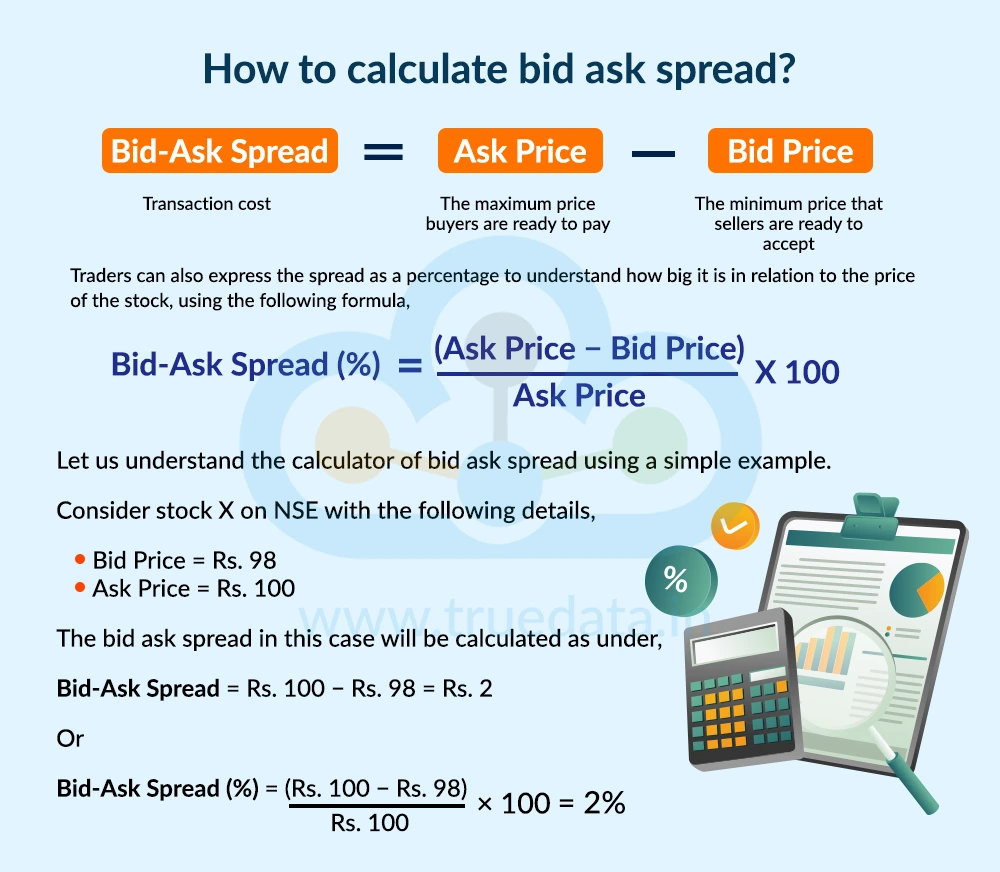
The bid-ask spread is calculated by subtracting the bid price from the ask price. It tells the difference between the price buyers are willing to pay and the price sellers want to receive. This spread is a key factor in trading because it affects trading costs and the ease of buying or selling a stock.
The formula to calculate the bid-ask spread is,
Bid-Ask Spread = Ask Price − Bid Price
Traders can also express the spread as a percentage to understand how big it is in relation to the price of the stock, using the following formula,
Bid-Ask Spread (%) = (Ask Price − Bid Price) / Ask Price × 100
Let us understand the calculator of bid-ask spread using a simple example.
Consider stock X on NSE with the following details,
Bid Price = Rs. 98
Ask Price = Rs. 100
The bid-ask spread in this case will be calculated as under,
Bid-Ask Spread = Rs. 100 − Rs. 98 = Rs. 2
Or
Bid-Ask Spread (%) = (Rs. 100 − Rs. 98) / Rs. 100 × 100 = 2%
This means the spread is Rs. 2 or 2% of the stock price. For traders, this helps understand how much extra cost is involved in a trade. A smaller spread (like 0.1% or Rs. 0.10) means the stock is very liquid and cheap to trade, while a larger spread means it might be harder or more expensive to trade quickly.
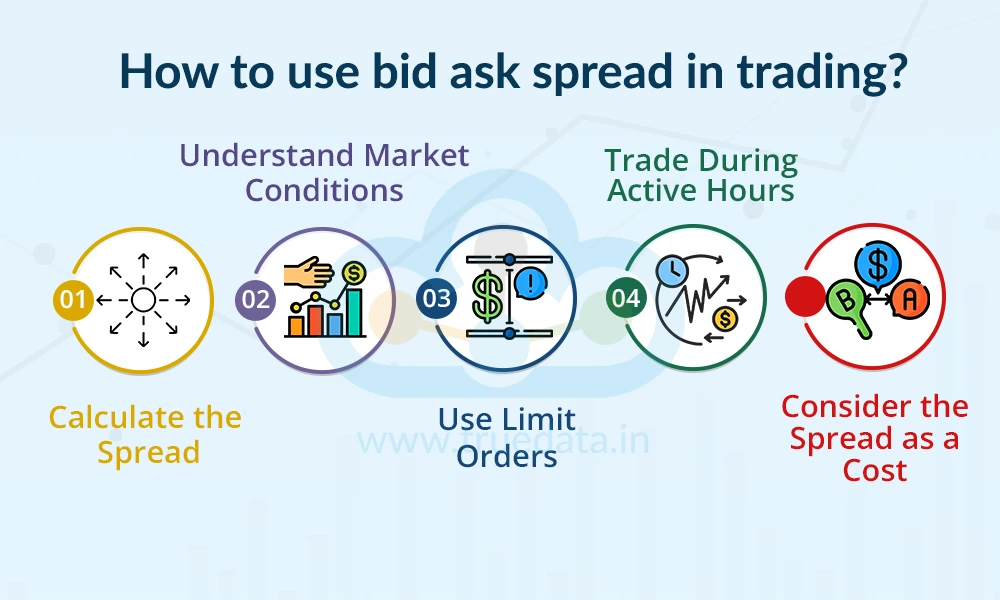
The steps to use the bid-ask spread in trading begin with checking the current bid (buy) and ask (sell) prices shown on the trading platform. The steps for trading using the bid-ask spread then include,
Calculate the Spread - The spread is found by subtracting the bid price from the ask price. A smaller spread usually indicates high liquidity and lower trading costs, while a larger spread suggests the opposite.
Understand Market Conditions - Tight spreads often appear in actively traded stocks and are suitable for quick trades. Wider spreads may indicate lower volume and higher risk.
Use Limit Orders - Instead of placing market orders, traders should use limit orders to control the price at which they buy or sell. This helps avoid paying the full spread unnecessarily.
Trade During Active Hours - Trading during high-volume periods, such as early market hours (between 9:15 AM and 11:30 AM IST), often results in tighter spreads and better pricing.
Consider the Spread as a Cost - Even in low or zero brokerage environments, a wide bid-ask spread can act as a hidden cost and reduce profits.

The bid-ask spread is an important aspect of technical analysis and understanding price movements. Here is a brief insight into the importance of bid-ask spread and how it can help traders.
Shows Market Liquidity - The bid-ask spread tells how easy it is to buy or sell a stock. A small spread means there are many buyers and sellers, so the stock is liquid and can be traded quickly. A large spread means fewer participants, and it may be harder to exit a trade fast.
Affects Trading Costs - Even if there is zero brokerage, a wide bid-ask spread increases the cost of trading. For example, if someone buys at Rs. 100 and can only sell at Rs. 98, they immediately lose Rs. 2. A smaller spread means lower cost and better profit potential.
Helps Decide Entry and Exit Points - By looking at the bid and ask prices, a trader can plan better entry and exit points. Placing limit orders between the bid and ask can help get a better price than just accepting the market rate.
Reflects Market Sentiment - The spread can show market mood and activity. A tight spread usually means the stock is active and in demand. A wide spread may signal uncertainty, low volume, or low interest from traders.
Useful for Intraday and Short-Term Traders - The bid-ask spread is very important for day traders or scalpers. Since they make small profits on quick trades, even a small spread can affect their overall return. They prefer stocks with narrow spreads and high volume.
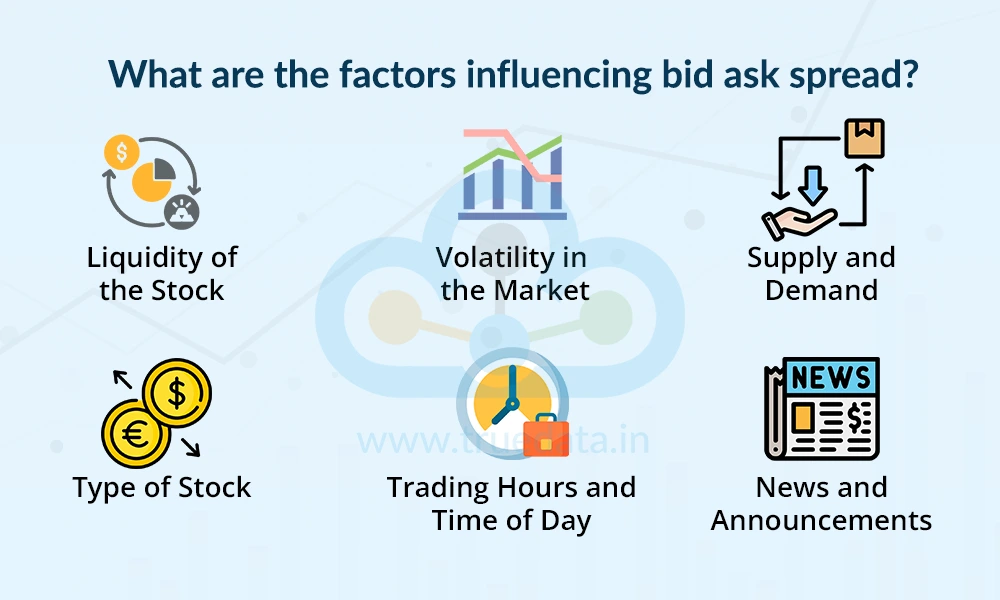
The bid-ask spread is essentially the result of the presence of buyers and sellers. However, it is affected by various factors. Some of the factors that affect the bid-ask spread include,
Liquidity of the Stock - Stocks that are traded frequently and have high volume usually have a narrow (small) bid-ask spread. This is because there are many buyers and sellers. On the other hand, illiquid stocks (low trading activity) tend to have wider spreads, making them more expensive to trade.
Volatility in the Market - When a stock or the overall market is highly volatile, spreads tend to widen. This is because both buyers and sellers are unsure about the fair price and want to protect themselves from sudden price changes. Stable markets usually have tighter spreads.
Supply and Demand - If more people are buying a stock than selling it, the bid price goes up, and the spread can change. Similarly, if there are more sellers than buyers, the ask price may fall. So, the balance between buyers and sellers affects the spread.
Type of Stock - Large-cap and blue-chip stocks like Reliance, TCS, or Infosys usually have small spreads because they are actively traded. In contrast, penny stocks or small-cap stocks may have larger spreads due to low interest and lower volumes.
Trading Hours and Time of Day - The spread is usually tighter during peak market hours (like 9:30 AM to 11:30 AM IST) when trading activity is high. It may become wider near market opening and closing, or during off-peak hours due to less participation.
News and Announcements - Important news, such as earnings reports, government policies, or global events, can cause uncertainty. During such times, the spread may widen because traders are unsure about how the market will react.
The bid ask spread is the difference between the price according to the buyers' and the sellers' perception, and ultimately reflects the market demand. Traders can use this to assess the liquidity for a stock or an asset and find profitable trading opportunities with optimal entry and exit points. Thus, understanding the bid-ask spread helps traders reduce the hidden costs and make smarter trading decisions.
This blog talks about the basics of technical analysis, enabling traders to understand the nuances of trading. Let us know your thoughts on this topic or if you need any further information on the same, and we will address it.
Till then, Happy Reading!
Read More: Open Interest in the Stock Market

The Japanese Yen (JPY) has long been one of the world’s major currencies, ...

The stock market in India has fascinated general Indian masses for long, perhap...

Options trading is a dynamic and complex arena, filled with intricacies like opt...