
The financial statements of a company are the window into its financial health. Therefore, understanding these financial statements is crucial for all stakeholders to evaluate the company and its financial viability. We have discussed the meaning and need for consolidated financial statements in our previous blog. In this blog, we will explore the standalone statements and the difference between the two sets of financial statements.
Standalone statements are the financial reports or financial statements of a single company showing only its own financial performance and position presented for a particular interim period or on an annual basis. Unlike the consolidated financial statements, these reports do not include financials from the sister companies or any of their subsidiaries, joint ventures, or associate companies that are part of the same group. These financial statements help in understanding the financial health of the company, enabling an effective comparison with past performance as well as its peers. Companies are required to prepare these statements under the Companies Act, 2013 and in accordance with the prescribed Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS).

Standalone statements give an insight into the company’s financial performance during the notified period and help the relevant stakeholders take necessary remedial actions if needed. The need for a standalone statement is explained hereunder.
Standalone statements help investors see how the main company is performing without the impact of its subsidiaries or joint ventures. This is useful when investors want to analyse the strength and profitability of the core operations alone.
Preparing and presenting both the standalone and consolidated financials shows that the company is being transparent and fulfilling all the compliance requirements. It builds trust with shareholders, regulators, and the public.
Companies must prepare standalone financial statements under the Companies Act, 2013 as part of the basic legal obligation, even if the company also prepares consolidated financial statements.
Since standalone statements show only one company’s results, investors can more easily compare similar companies in the same industry without being confused by additional businesses or investments.
Investors can understand the company’s own debts, profits, and risks by looking at only the parent company’s financials. This helps them make smarter investment decisions based on the main business, not on other companies it owns.
Companies use standalone statements to track the individual performance of the parent company. This helps management plan better, control costs, and make decisions for future growth.
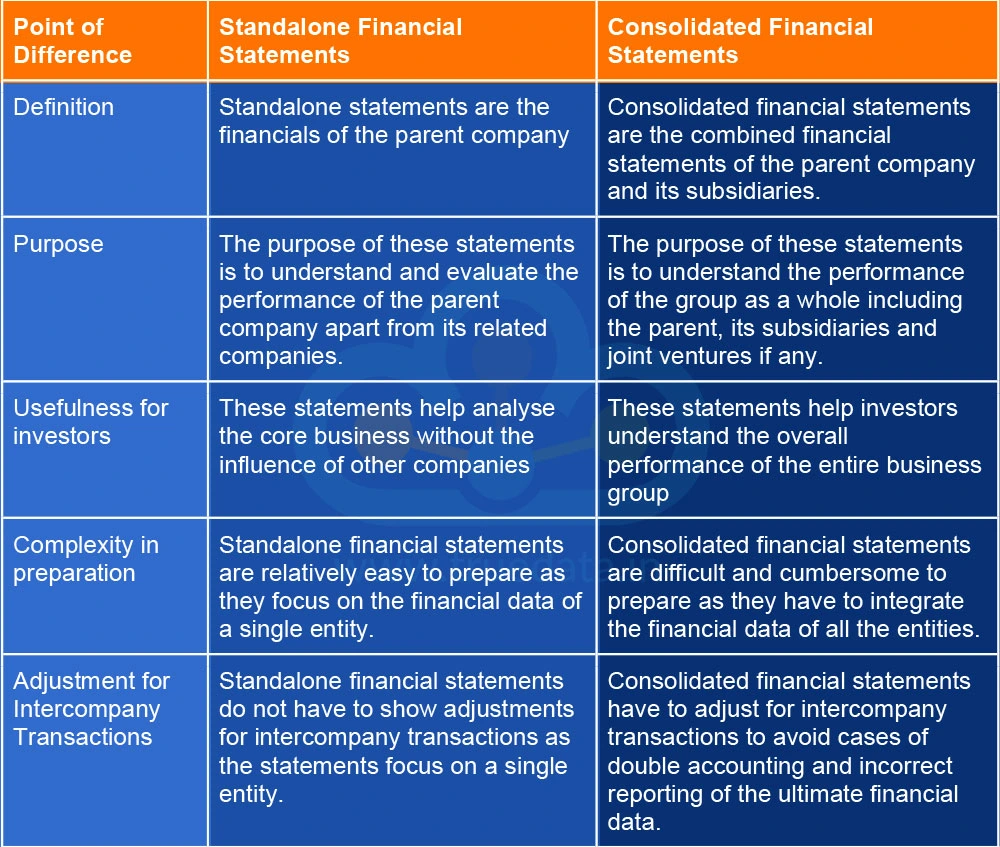
The standalone financial statements and the consolidated financial statements are integral parts of a company. However, these sets of statements serve different purposes and cater to different audiences as well. The key differences between these statements are explained below.
The use and the purpose of preparing the standalone financial statements are different as compared to showing the consolidated data of the entire group organisation as a whole. However, in order to effectively get the necessary insights from these statements, it is important to understand the pros and cons of using the standalone statements. Here is a brief analysis of the same.
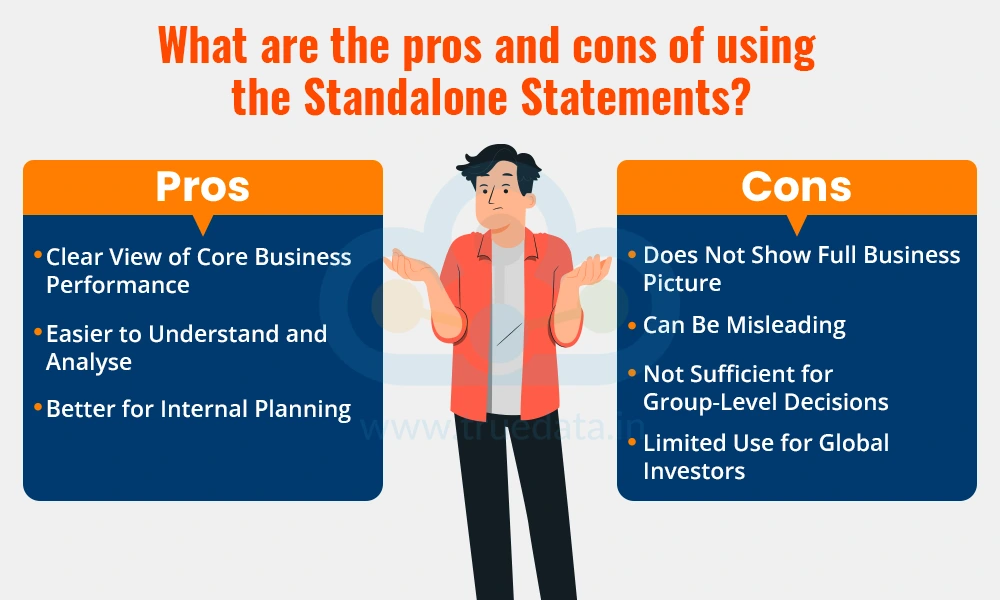
Clear View of Core Business Performance - Standalone statements help investors and company owners see how the main business is doing without the impact of subsidiaries or other related companies. This is useful for tracking the true performance of the parent company.
Easier to Understand and Analyse - Since only one company is involved, the data is less complicated. This makes it easier for small investors, analysts, or management to review and make decisions based on profits, debts, and cash flows.
Better for Internal Planning - Companies can use these statements to evaluate their own business operations and make decisions related to budgeting, investments, and cost control.
Does Not Show Full Business Picture - Standalone statements leave out the performance of subsidiaries, joint ventures, or associate companies. So, investors do not get the complete picture of the entire business group’s strength or risk.
Can Be Misleading - If a company has many successful or loss-making subsidiaries, ignoring them in the financial analysis may result in incorrect conclusions about the company’s true performance.
Not Sufficient for Group-Level Decisions - For large business groups, management and investors need consolidated statements to understand how the entire group is performing together. Standalone data on its own is not enough.
Limited Use for Global Investors - International or institutional investors usually prefer consolidated financials because they reflect the overall strength of the company and its global operations.
Standalone financial statements are important reports that show how a company is performing on its own, without including the results of its subsidiaries or joint ventures. They are simple, easy to understand, and help investors and company managers focus on the core business. However, these statements do not give the complete picture of the organisation, especially if there are multiple entities in the group.
This topic was an attempt to simplify a core concept of the financial data analysis of a company. Let us know if you need further information on this topic or have any insights of your own.
Till then, Happy Reading!
Read More: How to Read Annual Report?

Thestock market never stands still, and prices swing constantly with every new h...

Net profits in the P&L statement are usually a sign of a healthy company. Ho...

Theprofit and loss statement is the second part of the company's financial state...