
The stock markets are experiencing a blood bath across the world due to the Trump Tariffs. However, this has provided a good opportunity for long-term investors to buy good quality stocks for their portfolio. But how do you pick good quality stocks? The answer is in their fundamental analysis, which compares the value of the stock to its intrinsic value. Have you heard of this term? Read on to learn the meaning of the intrinsic value of shares and their importance in stock selection.
The intrinsic value of shares is a method of valuation of the shares and thereby the business as a whole. The key factor in this valuation is that the value of shares is determined based on the actual financial health of the company, rather than simply its current value of shares, which is based on market forces of demand and supply. The intrinsic value of shares is calculated by analysing various factors like the company earnings, debt levels, expected growth rate and future cash flows. This helps investors decide the true worth of the company and thereby the price to pay for its shares.
The intrinsic value of shares is often said to be the ultimate way to ascertain the true worth of a company. It is an important tool for investors and the company alike to understand the company's valuation and its relative position in the industry. The importance of the intrinsic value of shares and their use for important stakeholders is explained below.

Understanding the intrinsic value of a share is very helpful for investors in making smart investment decisions. The price of a stock in the market is affected by numerous factors like the news, market trends, or public sentiment, which may not reflect the actual condition of the company. Relying solely on the market price may lead to paying too much for the stock or selling too early. However, knowing the intrinsic value can help in comparing it with the current market price to make informed investment decisions. If the market price is lower than the intrinsic value, it may be a good chance to buy and hold for long-term gains. On the other hand, if the market price is much higher than the intrinsic value, it could be a sign of overvaluation and risk. Thus, intrinsic value helps investors avoid losses, choose better stocks, and invest with confidence, especially in a growing economy like India with volatile stock markets.

Knowing the intrinsic value is equally important for companies, as it enables strategic intervention if needed. A company with shares trading significantly lower than its intrinsic value might send the wrong message to the market that the company is weak or not doing well. This could affect its reputation, lower investor trust, and make it harder to raise money in the future. In such situations, the company might take steps like improving financial transparency, communicating better with investors, or even buying back its own shares to boost confidence. On the other hand, if a company’s shares are trading far above their intrinsic value, it may lead to unrealistic expectations from investors, and if the performance does not match, the share price might fall suddenly. Hence, knowing and maintaining a balance around the intrinsic value helps the company build long-term trust, attract serious investors, and grow steadily in the competitive Indian market.
The calculation of the intrinsic value of shares is a fundamental concept and among the first steps in the valuation of a company. There are many methods to calculate the intrinsic value of shares that can be used by investors to determine the true worth of the company. These methods are discussed below.
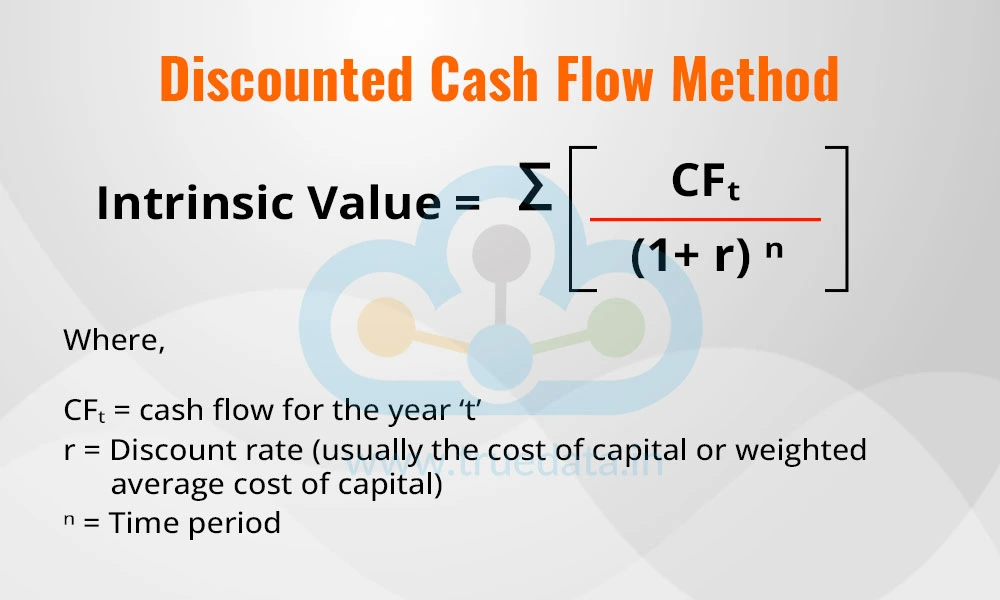
This method of calculating the intrinsic value of shares uses the present value of all future cash flows a company is expected to generate. This method is widely used by investors and other stakeholders (like lenders) to evaluate the company’s actual worth. This method starts by forecasting the company's future cash flows for several years. These values are then discounted at the cost of capital or rate or return to their present value, which accounts for the time value of money and risk. Finally, the resultant discounted cash flow values are summed up to get the intrinsic value.
The formula for calculating the intrinsic value through the DCF method is,
Intrinsic Value = ∑ [CF? / (1+ r) n]
Where,
CF? = cash flow for the year ‘t’
r = Discount rate (usually the cost of capital or weighted average cost of capital)
n = Time period
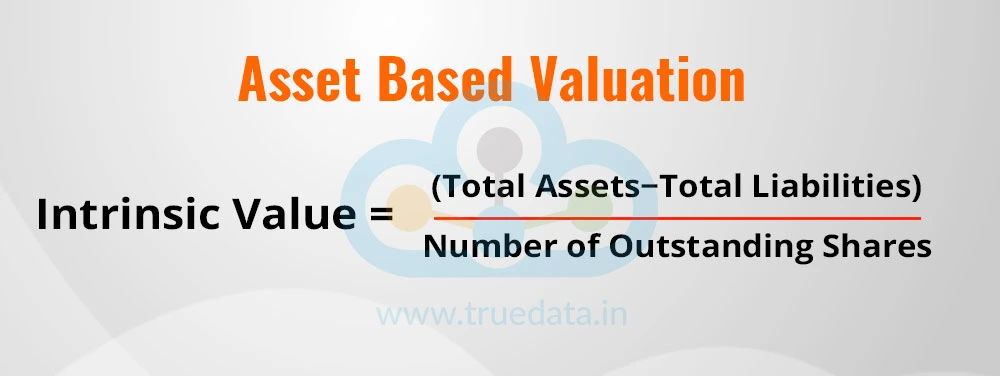
This is the easiest method to calculate the intrinsic value of shares. This method uses the company’s net assets and the net liabilities to arrive at the share’s intrinsic value by deducting the total liabilities from the total assets of the company. The resultant value is the net assets of the company, which are then divided by the total outstanding number of shares.
The formula for calculating the intrinsic value of shares using the asset-based valuation is,
Intrinsic Value = (Total Assets − Total Liabilities) / Number of Outstanding Shares
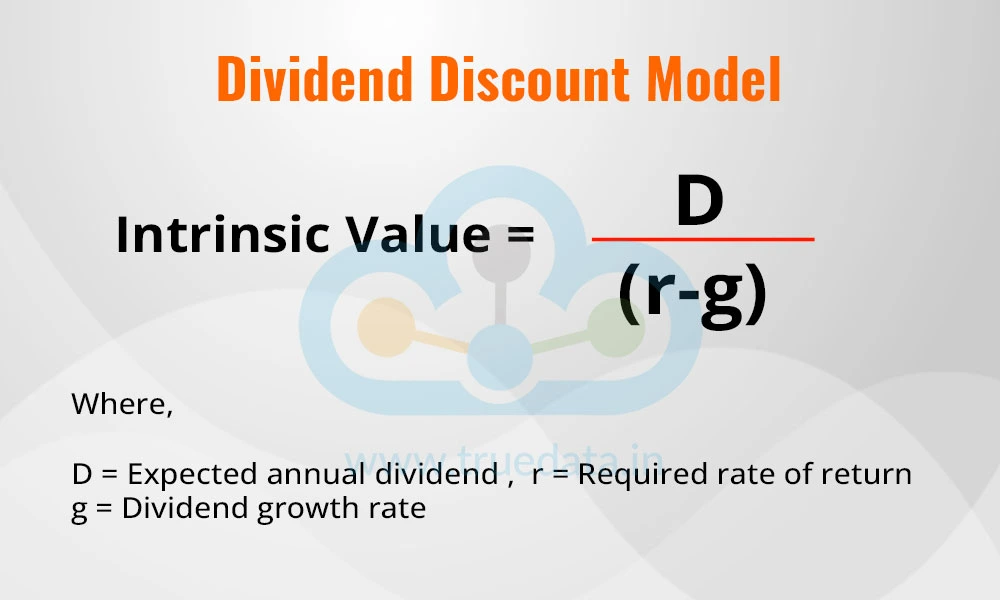
The Dividend Discount Model is useful for companies that pay regular and predictable dividends. It calculates the present value of expected future dividends. The DDM assumes that the value of a stock is the sum of all future dividends, discounted to their present value. It works best for stable companies with predictable dividend growth.
The formula to calculate the intrinsic value of shares using the DDM is,
Intrinsic Value = D / (r-g)
Where,
D = Expected annual dividend
r = Required rate of return
g = Dividend growth rate
Book Value and Market Value are two important valuation concepts for investors to understand when evaluating a company's worth. The meaning of these terms and their significance are explained below.

Book Value is the value of a company or its net worth according to its balance sheet. It shows how much the company would be worth if it sold all its assets and paid off all its debts. In other words, it reflects the accounting value of a company and not its market price. Book value helps find out whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued. If the market price of a stock is much lower than the book value or intrinsic value, the stock may be undervalued, especially if the company is healthy and profitable. The formula to calculate the book value of shares is,
Book Value of Shares = (Total Assets − Total Liabilities) / Number of Outstanding Shares

Market Value, also known as Market Capitalisation (Market Cap), is the price at which the company is currently being valued by the stock market. Market Value reflects how much investors are willing to pay for the company in the stock market right now and changes constantly as share prices go up and down. It is influenced by factors like investor sentiment, future growth expectations, and market conditions, along with the financial statements.
The formula to calculate the market value of shares is,
Market Value of Shares = Current Share Price * Total Number of Shares Outstanding
Now that we have seen the meaning of all three terms or modes of valuing the shares of a company, let us now consider the basic differences between the three and when are they used.
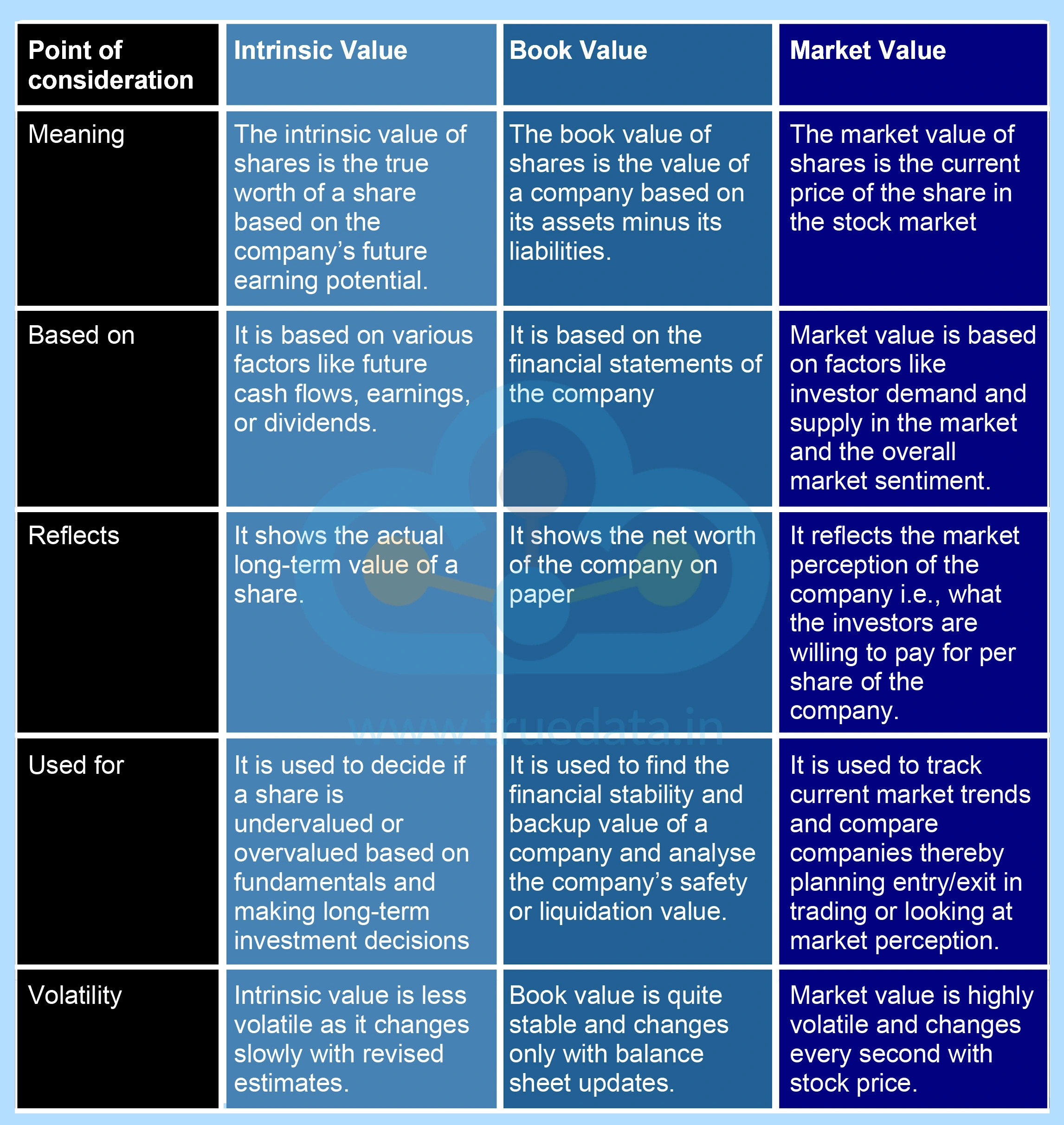
The intrinsic value is the true measure of the company's valuation that enables the stakeholders to make strategic decisions for investment and optimising company resources. The calculation of intrinsic value can be quite challenging for average investors, especially through the DCF method, however, it reflects the correct valuation and parameters for comparing the current market value of shares. This helps investors shape profitable portfolios and weed out stocks that are overvalued and fundamentally no longer strong.
This article is another addition to our series on understanding a key concept of the fundamental analysis of a company. Let us know your thoughts on this topic, or if you need further information, and we will address it.
Till then, Happy Reading!
Read More: Corporate Actions and their Impacts on Share Prices

Thestock market never stands still, and prices swing constantly with every new h...

Every company has a core group of people who believe in its vision from day one,...

Imagine a business without any competition. What's the outcome? An unchecked mon...