 On February 1st, 2023, the Honourable Finance Minister Mrs. Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Union Budget for 2023-24 for the 5th time in the Parliament. There were many eyes on this budget as expected as this was the last full year budget of Modi Government 2.0 and it is safe to say that it did not disappoint the public at large. Many significant announcements were part of this budget from the micro as well as macro growth perspectives and this budget is said to have laid the foundation for the Amrit Kaal of the country i.e., the groundwork for developed India in the next 25 years. The budget highlighted 7 key areas of priority for the government ‘Saptarishi’ with the vision for the Amrit Kaal. These priorities include Inclusive Development, Reaching the Last Mile, Infrastructure and Investment, Unleashing the Potential, Green Growth, Youth Power, and Financial Sector. The key highlights of this Budget 2023 are mentioned hereunder. Read More: Expectations from Budget 2023
On February 1st, 2023, the Honourable Finance Minister Mrs. Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Union Budget for 2023-24 for the 5th time in the Parliament. There were many eyes on this budget as expected as this was the last full year budget of Modi Government 2.0 and it is safe to say that it did not disappoint the public at large. Many significant announcements were part of this budget from the micro as well as macro growth perspectives and this budget is said to have laid the foundation for the Amrit Kaal of the country i.e., the groundwork for developed India in the next 25 years. The budget highlighted 7 key areas of priority for the government ‘Saptarishi’ with the vision for the Amrit Kaal. These priorities include Inclusive Development, Reaching the Last Mile, Infrastructure and Investment, Unleashing the Potential, Green Growth, Youth Power, and Financial Sector. The key highlights of this Budget 2023 are mentioned hereunder. Read More: Expectations from Budget 2023
The Finance Minister talked about taxation in the last part of the budget. However, let's discuss it at the very start as this is the most awaited and crucial part for any average taxpayer.
There have been 5 significant changes in direct taxes in Budget 2023. These changes and ancillary highlights are given below.
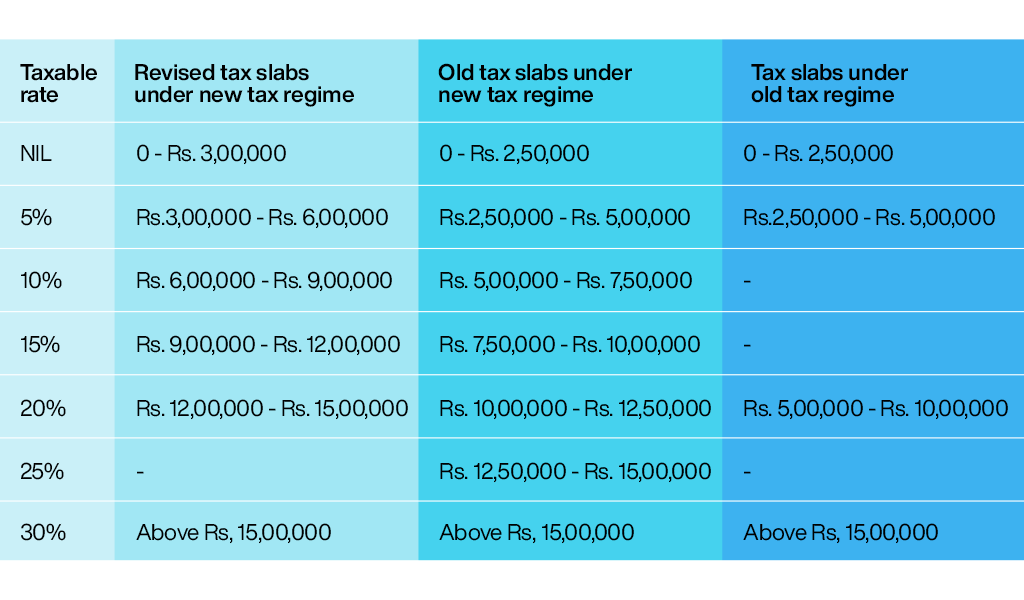
As mentioned above, the budget has revised the tax slabs under the new tax regime in an attempt to make it more attractive to the taxpayers. Let us consider net tax payable at various levels to understand the difference in tax liability under each scenario. 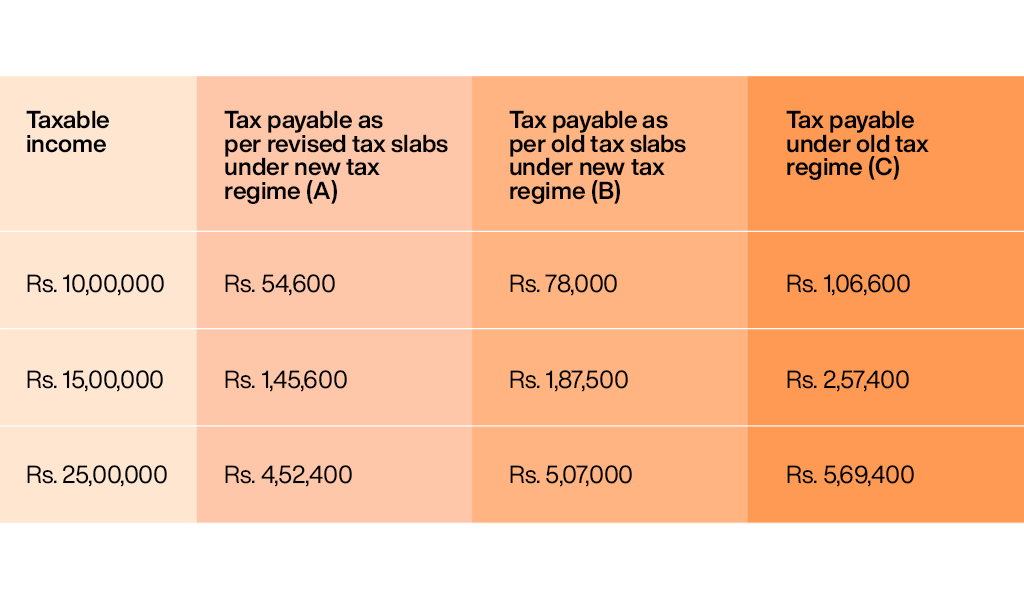 The above calculation is done after considering the standard deduction of Rs. 50,000 under A and C category and the same is not available under old slabs in the new tax regime. The final tax liability is after the addition of a health and education cess of 4% on the tax payable. Furthermore, taxpayers need to understand that the new tax regime does not provide the multiple benefits of deductions and exemptions which are still available in the old tax regime. Therefore, deductions like the 80C (Rs.1,50,000), 80D (Rs. 25,000 or Rs. 50,000), 80E, 80G, 80TTA, Section 24, etc. will significantly bring down the taxable income under the old tax regime ultimately reducing the tax liability.
The above calculation is done after considering the standard deduction of Rs. 50,000 under A and C category and the same is not available under old slabs in the new tax regime. The final tax liability is after the addition of a health and education cess of 4% on the tax payable. Furthermore, taxpayers need to understand that the new tax regime does not provide the multiple benefits of deductions and exemptions which are still available in the old tax regime. Therefore, deductions like the 80C (Rs.1,50,000), 80D (Rs. 25,000 or Rs. 50,000), 80E, 80G, 80TTA, Section 24, etc. will significantly bring down the taxable income under the old tax regime ultimately reducing the tax liability.
There have been a few changes in the indirect tax structure. The number of basic customs duty rates on goods, other than textiles and agriculture, reduced to 13 from 21. There have also been a few changes in the basic customs duty, cess, and surcharge on various commodities like toys, bicycles, automobiles, and naphtha. There has been a reduction in customs duty to boost domestic manufacturing. Some segments of products in this category include agricultural products, minerals, specified capital goods, IT and electronics, electronic appliances, and others. Some products that are going to get cheaper are mobile phones, TV panels, seeds in lab-grown diamonds, and shrimp feed. Some of the products that are going to get costlier are cigarettes, articles made by gold bars, fully imported luxury cars, and EVs as well as compounded rubber.
 There have been several changes in the corporate tax too which include extending the 15% corporate tax benefits to the new co-operatives that commence manufacturing till 31st March 2024. There has been an extension of the date of incorporation for another year for getting income tax benefits for start-ups. Apart from this, an increase in the benefit of the carry forward of losses on the change of shareholding of start-ups for 10 years from the existing 7 years of incorporation. The budget has also provided a higher limit of Rs. 3 crores for TDS on the cash withdrawal for co-operative societies. There has also been a provision of a higher limit of Rs. 2,00,000 per member for cash deposits to and loans in cash by Primary Agricultural Co-operative Societies (PACS) and Primary Co-operative Agriculture and Rural Development Banks (PCARDBs).
There have been several changes in the corporate tax too which include extending the 15% corporate tax benefits to the new co-operatives that commence manufacturing till 31st March 2024. There has been an extension of the date of incorporation for another year for getting income tax benefits for start-ups. Apart from this, an increase in the benefit of the carry forward of losses on the change of shareholding of start-ups for 10 years from the existing 7 years of incorporation. The budget has also provided a higher limit of Rs. 3 crores for TDS on the cash withdrawal for co-operative societies. There has also been a provision of a higher limit of Rs. 2,00,000 per member for cash deposits to and loans in cash by Primary Agricultural Co-operative Societies (PACS) and Primary Co-operative Agriculture and Rural Development Banks (PCARDBs).
This budget saw the highest allocation towards Capex which is to the tune of Rs. 10 lakh crores. This allocation is approximately 3.3% of the GDP and will be approximately 3 times the outlay that was made by the government in 2020. Railways also have been allocated a higher budget of Rs. 2.40 lakh crores. The government has also announced the providing 50-year interest-free loans to states that will help in continued infrastructure development. These loans are conditional that the capital investment and infrastructure be made by 2024. The government will also create an Urban Infrastructure Development Fund for the creation of urban infrastructure in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities. The government will also use the funds for improving regional air connectivity by developing 50 additional airports, heliports, water aerodromes, and advanced landing grounds. Some of the other important announcements for capital allocation and infrastructure development under Budget 2023 are given hereunder.
Budget 2023 also gave key insights into the total revenue and expenditure of the government in the coming year. The government also showed that it is on track with its fiscal deficit target to be below 4.5% by 2025-26. The fiscal deficit for 2023-24 is estimated to be 5.9% of the GDP which was also in line with the estimates as per many national and international reports. The government also announced that a fiscal deficit of 3.5% of GSDP will be allowed for States of which 0.5% is tied to Power sector reforms.
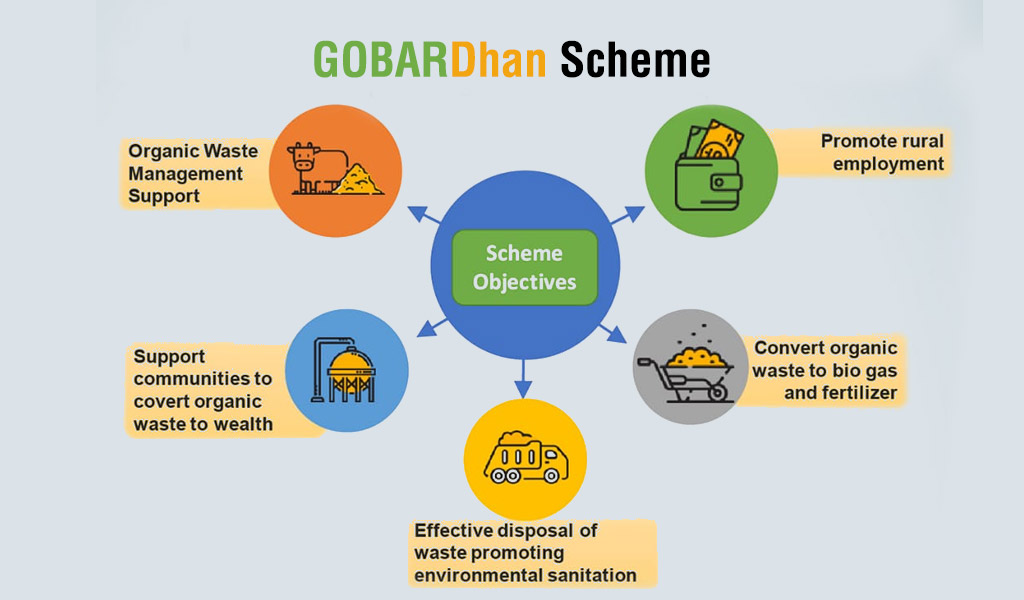 The government has announced many new initiatives with the target of green growth for the country. These initiatives include setting up 500 new ‘Waste to Wealth plants’ which will be established under the GOBARDhan Scheme. The government will also launch the PM-PRANAM to incentivise States and UTs to promote the usage of alternative fertilisers. The government has also planned to allocate ?35000 crore outlay for energy security, energy transition, and net zero objectives. Battery energy storage systems will also be promoted to steer the economy on the sustainable development path. Rs. 20,700 crore outlay will also be provided for renewable energy grid integration and evacuation from Ladakh.
The government has announced many new initiatives with the target of green growth for the country. These initiatives include setting up 500 new ‘Waste to Wealth plants’ which will be established under the GOBARDhan Scheme. The government will also launch the PM-PRANAM to incentivise States and UTs to promote the usage of alternative fertilisers. The government has also planned to allocate ?35000 crore outlay for energy security, energy transition, and net zero objectives. Battery energy storage systems will also be promoted to steer the economy on the sustainable development path. Rs. 20,700 crore outlay will also be provided for renewable energy grid integration and evacuation from Ladakh.
The Union Budget 2023 was held well on many parameters and the key outcome of the budget is the financial and growth outlay that it has laid for the next 25 years of the country. The strategic allocation to infrastructure and the country’s vision to be energy efficient have been showcased strongly through this budget. We hope this analysis article was able to provide you with the key details of the budget 2023 and what it holds for the average taxpayer. Do let us know if you want more details on the same or have any questions related to the changes in taxation. Till Then happy reading!

After the buzz around the general elections in India had just concluded, the sta...

The Budget Day in India is celebrated as a national event that every citizen awa...
The year 2023 is about to end in a month and it is almost time to set your new ...