
India's chemical industry stands at a pivotal point of growth and transformation, underpinned by robust domestic demand, strategic policy interventions, and opportunities to significantly expand global value chain participation. Valued at approximately USD 220 billion in 2023, the sector is anticipated to nearly double to USD 400-450 billion by 2030 and reach between USD 850 billion to USD 1 trillion by 2040. This sector, currently ranked sixth globally and third in Asia, contributes around 7% to India's GDP, supporting key sectors such as pharmaceuticals, agriculture, textiles, and automotive. However, India's share in global chemicals consumption remains modest at 3-3.5%, highlighting immense growth potential contingent on strategic policy actions.
The Indian chemicals market is highly diversified, segmented broadly into key categories such as petrochemicals, specialty chemicals, inorganic chemicals, and other vital products like fertilizers and pharmaceutical intermediates. Each segment exhibits distinct growth drivers and market dynamics, contributing to the sector's overall resilience and potential.
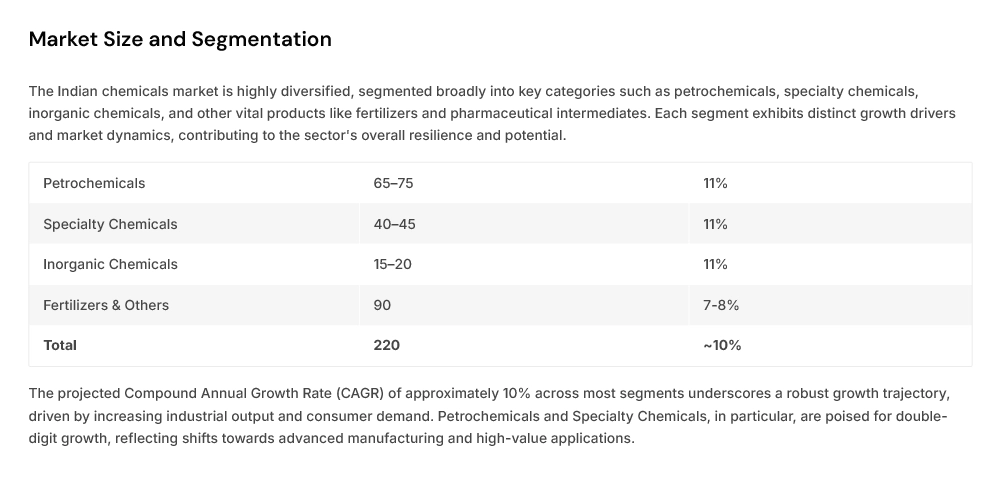
The projected Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 10% across most segments underscores a robust growth trajectory, driven by increasing industrial output and consumer demand. Petrochemicals and Specialty Chemicals, in particular, are poised for double- digit growth, reflecting shifts towards advanced manufacturing and high-value applications.
Several structural and macroeconomic tailwinds are expected to propel the Indian chemical industry into a new era of expansion. These drivers collectively create a fertile ground for sustained growth and increased market penetration, both domestically and globally.
Rising Household Incomes - With household consumption expected to add an astounding USD 1.5 trillion by 2030, the demand for chemical-derived products across various industries-from consumer goods to construction - is set to surge. This upward mobility in economic status translates directly into higher consumption of value-added chemicals.
Urbanization & Evolving Preferences - Rapid urbanization and changing consumer lifestyles are fueling a growing demand for specialty chemicals. These are crucial components in sectors like pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and advanced agrochemicals, reflecting a societal shift towards higher- quality and more sophisticated products.
India's rising share in global chemical value chains, projected to reach 536% by 2030, is further underpinned by supportive government initiatives including Production-Linked Incentives (PLI), the Make in Indiaî campaign, and the Aatmanirbhar Bharatî (Self-Reliant India) initiative. These policies aim to boost domestic manufacturing, reduce import dependency, and integrate India more deeply into global supply networks.
The Indian chemical industry is characterized by a dynamic mix of large-scale petrochemical producers and highly specialized players in niche chemical segments. Historically, India's chemical manufacturing has disproportionately focused on upstream commodities, creating a significant gap in value-added downstream specialty chemicals, which offer higher margins and greater global competitiveness.
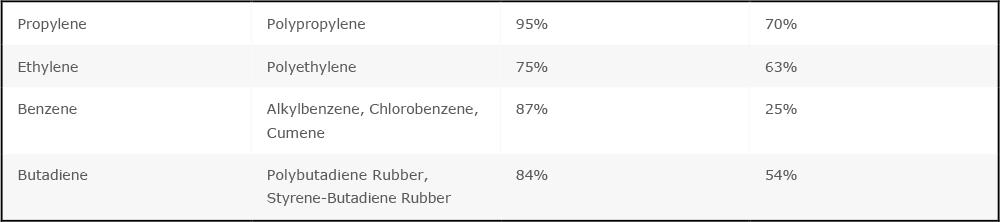
This feedstock utilization disparity highlights a critical opportunity for India to pivot towards high-value downstream manufacturing. By reducing reliance on commodity-grade output and increasing the production of specialty chemicals, India can enhance its global competitiveness, capture higher margins, and solidify its position as a diversified chemical manufacturing hub.
The regulatory environment has historically posed challenges for India¾s chemical sector, primarily due to complex environmental clearances, cumbersome procedural bottlenecks, and limited availability of key feedstocks. However, the government's renewed policy push aims to address these issues through targeted and structured interventions, fostering a more conducive ecosystem for growth and investment.
Establishment of Chemical Hubs - Inspired by successful international models like Jurong Island in Singapore, India plans to establish specialized chemical hubs. These integrated zones will centralize infrastructure, enhance logistical efficiency, and provide a single-window clearance system, thereby attracting both domestic and foreign investments into the sector.
Production-linked Incentives (PLI) & VGF - Financial mechanisms such as Production-Linked Incentives (PLI) and Viability Gap Funding (VGF) are being deployed. These schemes are designed to stimulate incremental domestic production, reduce import dependency, and provide crucial support for the development of high-value specialty chemical segments.
These strategic interventions are critical for transforming the regulatory landscape into an enabler of growth, rather than a barrier, positioning India as a more attractive destination for chemical manufacturing investments.

Despite being Asia's third-largest chemical producer, India's participation in the global market is still limited, especially when compared to China, which commands an impressive 33-35% of global chemical production. India's strategic intent is to emulate China's successful model, leveraging its competitive advantages such as lower labor costs, robust policy support, and targeted incentives to significantly scale domestic chemical manufacturing capabilities and enhance its global footprint.
This substantial net trade deficit underscores the urgent need to reduce import dependency and aggressively enhance exports, particularly in high-value specialty chemicals. Achieving net-zero imports by 2030 is a key national objective that would significantly bolster India¾s economic stability and global trade position.
By strategically focusing on value-added products and fostering a competitive manufacturing environment, India aims to become a formidable player in the global chemical landscape, contributing significantly to both domestic economic growth and international trade balances.
The NITI Aayog report provides a comprehensive strategic roadmap for the Indian chemical sector, structured around four core pillars. These pillars are designed to synergistically enhance competitiveness, foster innovation, and drive sustainable growth, ultimately positioning India as a global chemical powerhouse.
Export Growth - Capitalize on existing strengths and expand market share in global demanding chemical categories such as agrochemicals, dyes, and other intermediates where India has a competitive edge.
Emerging Segments -Strategically invest in sunrise sectors like battery chemicals, driven by the accelerating transition to renewable energy and the electric vehicle revolution, ensuring future-ready manufacturing capabilities.
Enhancing Competitiveness - Address structural gaps through targeted support and incentives for downstream, high-value production of essential chemicals like styrene and phenol, moving up the value chain.
Despite the overwhelmingly favorable outlook, the Indian chemical sector is not without its share of formidable headwinds. Addressing these challenges proactively will be crucial for unlocking the sector's full potential and ensuring a sustainable growth trajectory.
Feedstock Availability - A significant reliance on imports for key intermediates and raw materials exposes the sector to global price volatility and supply chain disruptions, necessitating strategies for domestic sourcing and backward integration.
Infrastructure Bottlenecks -Inadequate specialized logistics infrastructure, including storage, transportation, and port facilities tailored for chemicals, can impede efficiency and increase operational costs, requiring targeted investment in modernization.
Regulatory Complexity - Despite recent efforts, environmental compliance remains intricate, and procedural inefficiencies can still lead to delays in project approvals and expansions, necessitating further simplification.
India's chemical industry offers a compelling investment proposition, firmly anchored by solid structural growth drivers, targeted government interventions, and vast untapped opportunities in high-value chemical segments. The confluence of increasing domestic demand and a strategic push towards global integration creates an exceptionally favorable environment for investors.
Strategic investments in infrastructure, technological capabilities, and well-calibrated policy incentives provide a robust pathway toward achieving global competitiveness and sustaining long-term growth. This multifaceted approach is designed to transform India into a global chemical manufacturing hub.
For institutional investors, a selective approach is highly recommended. The focus should be on companies that are actively transitioning towards downstream, specialty, and higher-margin chemicals. These entities are best positioned to leverage the prevailing policy tailwinds, drive technological advancement, and adapt effectively to evolving global trade dynamics. Such strategic investments promise not only significant returns but also contribute to India's broader economic transformation.
India's chemical sector is positioned for sustained outperformance, making it a key growth engine in India's broader economic trajectory towards a USD 5 trillion economy.
Source: Adapted from "NITI Aayog Chemical Industry Report, July 2025"

We often hear Mr. Nitin Gadkariu saying that India will be a hub for electric v...

The recent Union Budget 2023 had a special focus on renewable energy and the go...

The IT sector has enjoyed huge growth over the past decades, however, the past ...